Medical / Drug Development
Connext Aims for Global Pharma Status with CNT201
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2025.10.02
※ Hongneung Small and Medium-Sized Special Zone is a medical, bio, and healthcare cluster equipped with academia, research, and hospitals, discovering and supporting deep-tech startups in various fields. Introducing promising deep-tech startups that will thrive in the global market based on South Korea.
The South Korean bio-pharmaceutical market is a landscape where growth and challenges coexist. New drugs such as Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC) and Cell and Gene Therapies (CGT) have emerged, opening up future possibilities, but changes in investment market trends have made stable research and development difficult. In the past, potential for future growth was enough to attract attention, but now only companies with clear clinical data and concrete commercialization strategies can survive.
In this context, there is a bio company that has developed a 'Best-in-Class' new drug with the weapon of microorganism-based recombinant protein manufacturing technology. The company is Connext, a developer of enzyme-based therapeutics.
Instead of entering the competition to discover new substances, Connext targeted a niche market where efficacy has been proven but manufacturing technology barriers are high, thus limiting competition. This is an approach that reinterprets innovation from a manufacturing process perspective rather than discovery. How did Connext establish and execute an optimized strategy in a difficult environment to create a new model for next-generation bio companies? A conversation with Lee Woo-jong, CEO of Connext, was held.
The Key to Microorganism-Based Biopharmaceutical Development is 'Manufacturing Process'
"I prepared for the startup with the belief that the key to developing new biopharmaceutical drugs using microorganism-derived substances is the manufacturing process. I wanted to improve the quality of life for patients by developing drugs in areas with high unmet needs compared to the oncology and immune disease fields."
Lee Woo-jong, who was researching biopharmaceutical manufacturing process development at the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology, founded Connext in 2017 with the dream of developing drugs to improve quality of life.
Connext aims to be a 'Specialty Pharma' targeting niche markets with unmet medical needs. To this end, it focused on securing recombinant protein production technology using microorganisms instead of animal cells. Microorganisms have a faster growth rate compared to animal cells, leading to higher productivity and lower manufacturing costs due to cheaper cultivation expenses. Connext strengthened its competitiveness based on its technical capabilities.
"New drug approval documents are divided into non-clinical, clinical, and manufacturing parts, and the manufacturing process is very important for biopharmaceuticals. Many biopharmaceuticals have completed clinical trials but failed to obtain FDA approval due to manufacturing issues."
CEO Lee Woo-jong repeatedly emphasized the importance of the manufacturing process in new drug development. Therefore, Connext has acquired the core development capabilities required for process development, scale-up, and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) production of recombinant proteins. It also operates a pilot facility with ISO 9001 certification, establishing a differentiation strategy centered on the manufacturing process. It has also secured capabilities related to non-clinical and clinical aspects and a network for commercialization.
CNT201, a 'Best-in-Class' New Drug Surpassing Competing Drugs
Connext has developed CNT201, a Recombinant Collagenase, and a Recombinant TLR5 Agonist. With these two drugs, it has established a diverse pipeline ranging from therapeutics to the aesthetic domain, enhancing corporate value. The threat to traditional bio-venture companies is the potential failure of commercialization due to the failure to prove the efficacy of new drug candidates. In contrast, Connext has reduced risk and secured competitiveness by improving drugs with already verified mechanisms of action.
The main drug is CNT201, which is being developed as a treatment for Dupuytren's contracture, a condition where collagen accumulates between the skin and tendons of the palm, causing fingers to remain bent. The only treatment for this condition is Endo's Xiaflex. Connext is developing CNT201 not as a biosimilar of Xiaflex but as a 'Best-in-Class' new drug with improved functionality.
The two drugs have different manufacturing methods. Xiaflex is produced by naturally fermenting the pathogenic bacterium Clostridium histolyticum, which secretes hemolytic toxins. In this case, there is a risk of hemolytic toxin contamination. In contrast, CNT201 is manufactured using genetic recombination technology in non-pathogenic host cells, eliminating the risk of hemolytic toxin contamination.
CEO Lee Woo-jong mentioned two strengths of CNT201. The first is its excellent safety. CNT201 is produced in non-pathogenic host cells through genetic recombination technology, ensuring high safety. This safety has been confirmed through clinical results, which CEO Lee Woo-jong explains as an example of how the manufacturing process improved the drug's safety profile.
The second strength is the convenience of formulation. Competing drugs use a 2-vial system where the lyophilized drug and its dedicated solvent are in separate vials, requiring a lengthy dissolution process by medical staff before use, which is inconvenient. However, CNT201 is a 1-vial lyophilized formulation that does not require a dedicated solvent. It dissolves with regular injectable water and has excellent storage stability. In addition to low manufacturing costs, it offers ease of use for medical staff. CEO Lee Woo-jong stated, "CNT201 is being developed as a 'Best-in-Class' new drug, not a biosimilar, through technological differentiation in the manufacturing of raw materials and finished products. If approved as a new drug, it is expected to secure market exclusivity for 12 years."
Connext, a small company with 18 employees, is conducting global development of CNT201. In June 2023, it received approval for a Phase 1/2 clinical trial plan (IND) from the US FDA, and successfully completed the Phase 1 dose-escalation part in April 2025. Subsequently, it plans to initiate the Phase 2 dose-expansion part in the fourth quarter of 2025 and secure top-line data by the first half of 2026. The goal is to find a partner and enter Phase 3 trials in 2027, ultimately launching the drug around 2030.
Aiming for CNT201 Commercialization by 2030, Pioneering the Global Market with New Drugs
Like other bio-venture companies developing new drugs, Connext faces two challenges. The first challenge is securing the necessary investment for development. CEO Lee Woo-jong stated, "Connext needs to secure funds to successfully carry out Phase 2 clinical trials and commercial manufacturing process development. However, due to recent global investment contraction, it is difficult to attract investment for bio-ventures."
The second challenge is securing specialized personnel. Currently, Connext is developing CNT201 in collaboration with global Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) and Clinical Research Organizations (CROs). However, as development becomes more advanced, specialized personnel with overall experience in new drug development are needed.
To solve various challenges and ensure sustainable growth, Connext has chosen to promote the excellence of CNT201. It plans to establish partnership agreements with countries such as Korea, Europe, and Russia based on the Phase 1 clinical data of CNT201 secured in April 2025. It intends to specifically negotiate contract terms with potential partners within 2025. After 2026, it plans to secure differentiated Phase 2 clinical data and enter the US market.
The company is also proceeding with the Initial Public Offering (IPO) process. It plans to apply for a technical evaluation required for a technology-special listing in 2026 based on Phase 2 clinical data and partnership achievements. Connext aims to sign a representative underwriting contract with Korea Investment & Securities in March 2025 and list on the KOSDAQ market in the first half of 2027.
The Hongneung Small and Medium-Sized Special Zone support program played an important role in Connext's global market entry. Connext, located in the Seoul Bio Hub Global Center, received various support such as technology transfer and investment attraction, laying the foundation for growth. Tailored support, including promotion, investment attraction linkage, and IPO-related support programs necessary for scale-up stage companies, was also provided. CEO Lee Woo-jong stated, "The Seoul Bio Hub Global Center is attractive not only for its working environment but also for its programs that help company growth. Thanks to extensive support, I believe the successful development of CNT201 and the expansion into overseas markets were possible."
"Starting with the commercialization of CNT201, we will accelerate the development of subsequent pipelines to become a globally specialized pharmaceutical company. As a company rooted in manufacturing processes, we plan to seek ways to create market opportunities by stably manufacturing and supplying therapeutics."
CEO Lee Woo-jong dreams of an integrated pharmaceutical company with its own production facilities, moving away from a structure dependent on external sources. To achieve this goal, efforts will also be made to establish a diverse new drug portfolio. Based on Connext's growth experience, it plans to contribute to creating a virtuous cycle ecosystem that helps other bio startups facing difficulties.
IT Donga Reporter Kang Hyung-seok (redbk@itdonga.com)
The South Korean bio-pharmaceutical market is a landscape where growth and challenges coexist. New drugs such as Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC) and Cell and Gene Therapies (CGT) have emerged, opening up future possibilities, but changes in investment market trends have made stable research and development difficult. In the past, potential for future growth was enough to attract attention, but now only companies with clear clinical data and concrete commercialization strategies can survive.
In this context, there is a bio company that has developed a 'Best-in-Class' new drug with the weapon of microorganism-based recombinant protein manufacturing technology. The company is Connext, a developer of enzyme-based therapeutics.
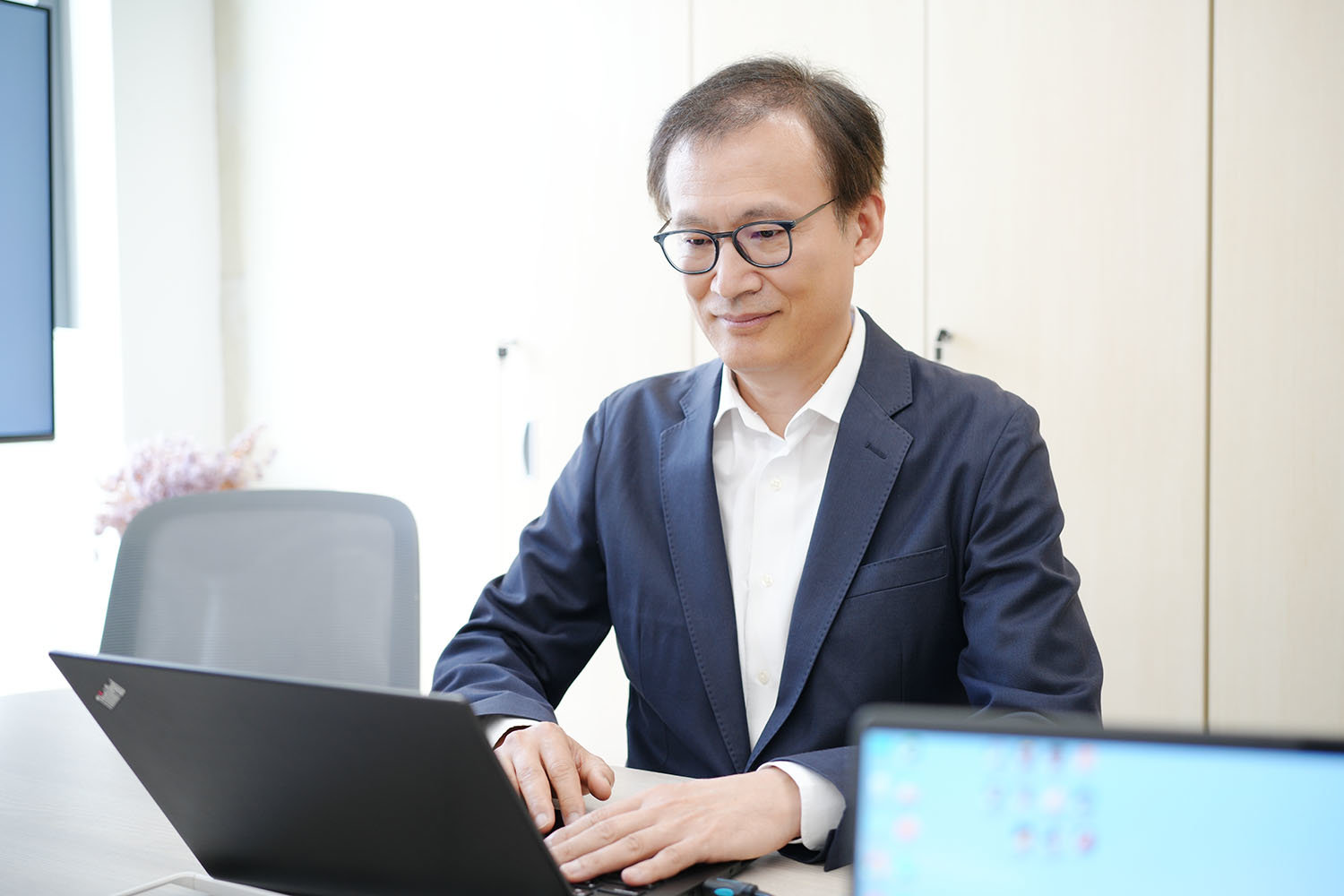
Lee Woo-jong, CEO of Connext / Source=IT Donga
Instead of entering the competition to discover new substances, Connext targeted a niche market where efficacy has been proven but manufacturing technology barriers are high, thus limiting competition. This is an approach that reinterprets innovation from a manufacturing process perspective rather than discovery. How did Connext establish and execute an optimized strategy in a difficult environment to create a new model for next-generation bio companies? A conversation with Lee Woo-jong, CEO of Connext, was held.
The Key to Microorganism-Based Biopharmaceutical Development is 'Manufacturing Process'
"I prepared for the startup with the belief that the key to developing new biopharmaceutical drugs using microorganism-derived substances is the manufacturing process. I wanted to improve the quality of life for patients by developing drugs in areas with high unmet needs compared to the oncology and immune disease fields."
Lee Woo-jong, who was researching biopharmaceutical manufacturing process development at the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology, founded Connext in 2017 with the dream of developing drugs to improve quality of life.
Connext aims to be a 'Specialty Pharma' targeting niche markets with unmet medical needs. To this end, it focused on securing recombinant protein production technology using microorganisms instead of animal cells. Microorganisms have a faster growth rate compared to animal cells, leading to higher productivity and lower manufacturing costs due to cheaper cultivation expenses. Connext strengthened its competitiveness based on its technical capabilities.
Connext focused on targeting niche markets with unmet medical needs / Source=Connext
"New drug approval documents are divided into non-clinical, clinical, and manufacturing parts, and the manufacturing process is very important for biopharmaceuticals. Many biopharmaceuticals have completed clinical trials but failed to obtain FDA approval due to manufacturing issues."
CEO Lee Woo-jong repeatedly emphasized the importance of the manufacturing process in new drug development. Therefore, Connext has acquired the core development capabilities required for process development, scale-up, and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) production of recombinant proteins. It also operates a pilot facility with ISO 9001 certification, establishing a differentiation strategy centered on the manufacturing process. It has also secured capabilities related to non-clinical and clinical aspects and a network for commercialization.
CNT201, a 'Best-in-Class' New Drug Surpassing Competing Drugs
Connext has developed CNT201, a Recombinant Collagenase, and a Recombinant TLR5 Agonist. With these two drugs, it has established a diverse pipeline ranging from therapeutics to the aesthetic domain, enhancing corporate value. The threat to traditional bio-venture companies is the potential failure of commercialization due to the failure to prove the efficacy of new drug candidates. In contrast, Connext has reduced risk and secured competitiveness by improving drugs with already verified mechanisms of action.
The main drug is CNT201, which is being developed as a treatment for Dupuytren's contracture, a condition where collagen accumulates between the skin and tendons of the palm, causing fingers to remain bent. The only treatment for this condition is Endo's Xiaflex. Connext is developing CNT201 not as a biosimilar of Xiaflex but as a 'Best-in-Class' new drug with improved functionality.
Connext has established a diverse pipeline including CNT201 Recombinant Collagenase and Recombinant TLR5 Agonist / Source=Connext
The two drugs have different manufacturing methods. Xiaflex is produced by naturally fermenting the pathogenic bacterium Clostridium histolyticum, which secretes hemolytic toxins. In this case, there is a risk of hemolytic toxin contamination. In contrast, CNT201 is manufactured using genetic recombination technology in non-pathogenic host cells, eliminating the risk of hemolytic toxin contamination.
CEO Lee Woo-jong mentioned two strengths of CNT201. The first is its excellent safety. CNT201 is produced in non-pathogenic host cells through genetic recombination technology, ensuring high safety. This safety has been confirmed through clinical results, which CEO Lee Woo-jong explains as an example of how the manufacturing process improved the drug's safety profile.
The second strength is the convenience of formulation. Competing drugs use a 2-vial system where the lyophilized drug and its dedicated solvent are in separate vials, requiring a lengthy dissolution process by medical staff before use, which is inconvenient. However, CNT201 is a 1-vial lyophilized formulation that does not require a dedicated solvent. It dissolves with regular injectable water and has excellent storage stability. In addition to low manufacturing costs, it offers ease of use for medical staff. CEO Lee Woo-jong stated, "CNT201 is being developed as a 'Best-in-Class' new drug, not a biosimilar, through technological differentiation in the manufacturing of raw materials and finished products. If approved as a new drug, it is expected to secure market exclusivity for 12 years."
Connext, a small company with 18 employees, is conducting global development of CNT201. In June 2023, it received approval for a Phase 1/2 clinical trial plan (IND) from the US FDA, and successfully completed the Phase 1 dose-escalation part in April 2025. Subsequently, it plans to initiate the Phase 2 dose-expansion part in the fourth quarter of 2025 and secure top-line data by the first half of 2026. The goal is to find a partner and enter Phase 3 trials in 2027, ultimately launching the drug around 2030.
Aiming for CNT201 Commercialization by 2030, Pioneering the Global Market with New Drugs
Like other bio-venture companies developing new drugs, Connext faces two challenges. The first challenge is securing the necessary investment for development. CEO Lee Woo-jong stated, "Connext needs to secure funds to successfully carry out Phase 2 clinical trials and commercial manufacturing process development. However, due to recent global investment contraction, it is difficult to attract investment for bio-ventures."
The second challenge is securing specialized personnel. Currently, Connext is developing CNT201 in collaboration with global Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) and Clinical Research Organizations (CROs). However, as development becomes more advanced, specialized personnel with overall experience in new drug development are needed.
To solve various challenges and ensure sustainable growth, Connext has chosen to promote the excellence of CNT201. It plans to establish partnership agreements with countries such as Korea, Europe, and Russia based on the Phase 1 clinical data of CNT201 secured in April 2025. It intends to specifically negotiate contract terms with potential partners within 2025. After 2026, it plans to secure differentiated Phase 2 clinical data and enter the US market.
The company is also proceeding with the Initial Public Offering (IPO) process. It plans to apply for a technical evaluation required for a technology-special listing in 2026 based on Phase 2 clinical data and partnership achievements. Connext aims to sign a representative underwriting contract with Korea Investment & Securities in March 2025 and list on the KOSDAQ market in the first half of 2027.
Lee Woo-jong, CEO of Connext / Source=IT Donga
The Hongneung Small and Medium-Sized Special Zone support program played an important role in Connext's global market entry. Connext, located in the Seoul Bio Hub Global Center, received various support such as technology transfer and investment attraction, laying the foundation for growth. Tailored support, including promotion, investment attraction linkage, and IPO-related support programs necessary for scale-up stage companies, was also provided. CEO Lee Woo-jong stated, "The Seoul Bio Hub Global Center is attractive not only for its working environment but also for its programs that help company growth. Thanks to extensive support, I believe the successful development of CNT201 and the expansion into overseas markets were possible."
"Starting with the commercialization of CNT201, we will accelerate the development of subsequent pipelines to become a globally specialized pharmaceutical company. As a company rooted in manufacturing processes, we plan to seek ways to create market opportunities by stably manufacturing and supplying therapeutics."
CEO Lee Woo-jong dreams of an integrated pharmaceutical company with its own production facilities, moving away from a structure dependent on external sources. To achieve this goal, efforts will also be made to establish a diverse new drug portfolio. Based on Connext's growth experience, it plans to contribute to creating a virtuous cycle ecosystem that helps other bio startups facing difficulties.
IT Donga Reporter Kang Hyung-seok (redbk@itdonga.com)
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News