Startup
Kira & Company: Fun Fintech Education with Kira
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2025.10.10
[Dongguk University Campus Town x IT Donga] Dongguk University Campus Town is collaborating with IT Donga to conduct the '2025 Scale-Up Program'. Dongguk University Campus Town and IT Donga will introduce the overall business activities of the startups participating in this program and analyze their business models. They aim to connect these startups with experts from various fields to help solve the challenges they face in advancing to the next stage.
Various financial products such as savings, investments, loans, and pensions are flooding the market, providing more opportunities for asset formation through financial products. As such, understanding economic trends and financial products and efficiently managing assets have become crucial, emphasizing the importance of 'financial literacy'. Carmine DI NOIA, Director of Financial and Enterprise Affairs at the OECD, stated, "Although the use of digital financial services such as online shopping and mobile payments has increased, financial literacy remains low. Governments should provide age-appropriate financial experiences and ensure equal financial education for all students to reduce the gap." Financial literacy is seen as playing a key role beyond individual financial knowledge, affecting the effectiveness of monetary policy, economic growth, and financial stability.
The financial literacy of Korean citizens is on the decline. According to the Financial Supervisory Service's national financial literacy survey data released in 2024, the financial literacy score of Korean adults was 65.7, slightly down from 66.5 in 2022. Notably, the score for young adults in their 20s was 59.5 in the 'financial behavior' category, lower than the scores of 64.2 to 68.4 recorded by those in their 30s to 60s.
The decline in financial literacy among elementary, middle, and high school students is also noteworthy. According to the 2024 economic literacy survey results for elementary, middle, and high school students announced by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance, sixth-grade elementary students scored 61.5, third-grade middle school students scored 51.9, and second-grade high school students scored 51.7. These scores represent declines of 3.9, 6.3, and 5.0 points, respectively, compared to 2022, with the exception of elementary students, failing to reach an average of 60 points. Analyzing the survey questions, the correct answer rates for practical life-related questions such as rational choice, e-commerce, and investment were high, but the rates for basic economic concepts and principles like inflation, supply and demand, and opportunity cost were low.
In the past, Koreans learned the financial structure through trial and error in society. They realize the need for financial education in the process of receiving wages, paying taxes, and taking loans. The problem is that the cost of trial and error is high. There are not a few cases where people lose assets accumulated over years due to wrong investment decisions or fall into excessive debt due to financial fraud.
However, financial education in Korea has just begun to take root. The Ministry of National Defense has decided to make economic education mandatory for military personnel starting in 2025, and the Ministry of Education will introduce a new subject on finance and economic life for second-year high school students in 2026. This contrasts with countries like the UK, the US, Japan, and Singapore, where public-private partnerships are conducting financial education for youth.
Advanced Countries Have Awakened to Financial Education
The UK is promoting financial education under the national goal of Financial Well-being. Since 2014, financial education has been integrated into the Personal, Social, Health, and Economic (PSHE) education curriculum. However, there are structural limitations in its implementation. PSHE is not a mandatory subject in all public schools, and financial education is selectively covered within the subject. Non-profit organizations have filled this gap in public education.
Financial education organizations such as My Bank and Money A+E operate tailored financial education programs for youth and adults. They secure funding through sponsorships from large financial institutions to ensure stable program operation. This is considered an exemplary case of how a public-private cooperation ecosystem can complement the limitations of public education.
Having experienced several financial crises, the US has reached a social consensus that individual financial soundness is directly linked to national economic stability. As a result, state governments have implemented strong policies requiring the completion of personal finance courses as a high school graduation requirement. As of 2024, 27 states are enforcing policies mandating the completion of finance courses.
US financial education focuses on practicality. It addresses real-world issues students will face immediately upon entering society, such as bank account management, the meaning of credit scores, student loans, and retirement preparation. The goal is not to produce economists but to cultivate financially independent citizens.
Japan significantly strengthened high school financial education in 2022, coinciding with the lowering of the adult age to 18. It teaches the characteristics of specific financial products such as stocks, bonds, and funds, and methods of asset formation, as well as national policies like the tax-free small investment system. In 2024, Japan established the Financial and Economic Education Promotion Organization (J-FLEC) with participation from the Financial Services Agency, the Bank of Japan, and private financial institutions. J-FLEC serves as the control tower overseeing national financial education.
Singapore's financial education focuses on integration. Although there is no separate financial subject, financial concepts are organically embedded throughout the curriculum. For example, budget management is taught during food and consumer education classes, while interest rates and taxes are covered in math classes. By incorporating financial concepts into the curriculum itself, it makes finance not a difficult academic subject but a basic life skill connected to all areas of life. Additionally, the Institute for Financial Literacy (IFL) provides financial education programs for the general public.
What About Financial Education in South Korea?
South Korea has also begun a major policy shift to enhance financial literacy among youth and young adults. The Ministry of National Defense will expand financial education for military personnel starting in 2025. This aims to prevent illegal sports gambling and excessive online payment behaviors as soldier salaries increase and smartphone use is permitted.
The Ministry of National Defense and the Financial Supervisory Service will expand the target of financial education from existing finance officers to all finance personnel, including non-commissioned officers and civilian employees. They plan to certify finance personnel as financial education instructors for military personnel, focusing on building internal education infrastructure. Financial education will address issues soldiers face in reality, such as asset management, voice phishing and cyber gambling prevention, understanding virtual assets, and pension planning.
The Ministry of Education will introduce a new elective subject on finance and economic life for second-year high school students starting in 2026, according to the revised curriculum. This subject will be reflected only in the school life record (admissions process) and not in the College Scholastic Ability Test, and will be an absolute evaluation subject. The finance and economic life subject consists of four courses: happy and safe financial life, income and expenditure, savings and investment, and credit and risk management, focusing on developing students' practical financial life skills.
Filling the Gap in Financial Education with Mobile and Gamification
The financial education policies of the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of National Defense are the foundation for future generations to enjoy a rational economic life. However, for financial education in South Korea to naturally expand, a digital financial education solution that is easily accessible to everyone is needed. To translate policy intentions into practical changes on the ground, educational tools and platforms that meet the future generation's expectations are necessary. Edu Fintech startup KIRA&Company proposes a solution that changes the paradigm of financial education by combining gamification and mobile learning (M-Learning).
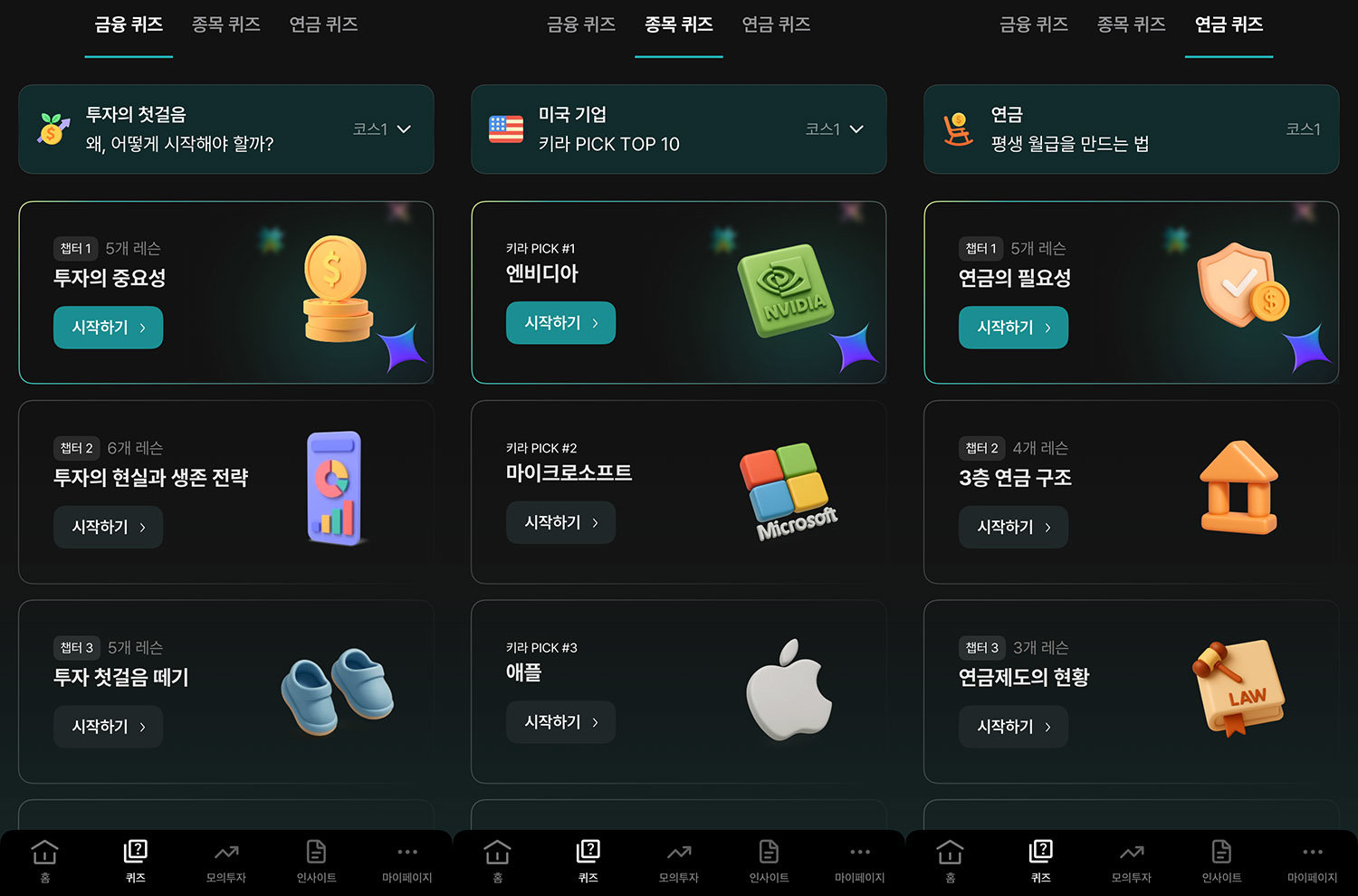
The mobile Edu Fintech service KIRA is designed to naturally acquire financial knowledge through an organic financial education system that could otherwise be tedious and challenging.
First, KIRA provides basic financial knowledge, individual stocks and cryptocurrencies, and the latest economic issues in short and fun quiz formats to help anyone easily learn financial knowledge. It builds learning-related habits through micro-learning. The content, organized by securities analysts and experts from the UK accounting field, enhances its completeness.
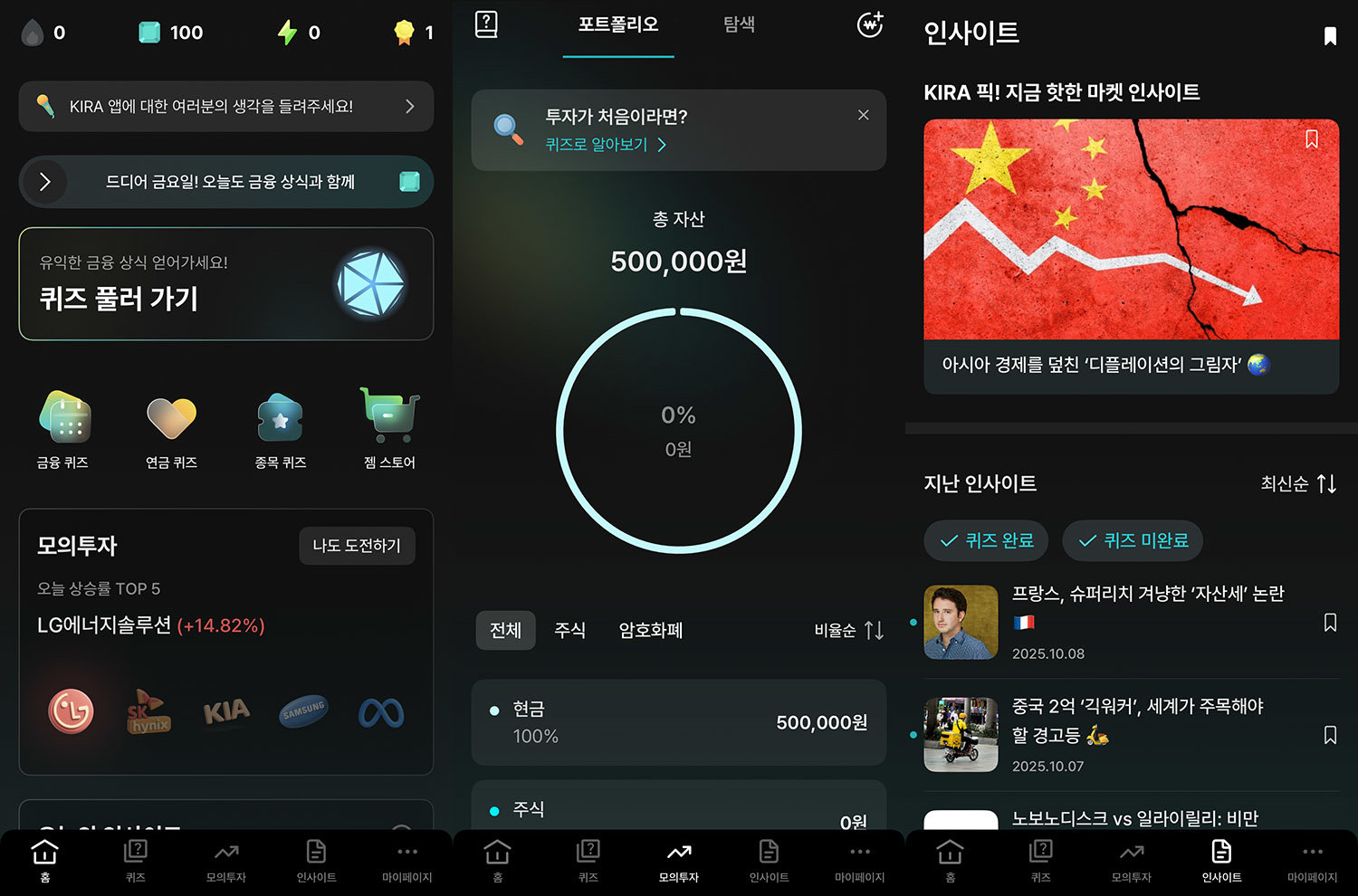
Next, the knowledge gained through quizzes can be immediately applied in a virtual environment (simulated investment) linked to real market data. This approach resolves the gap between theory and practice by experiencing the principles of complex financial products in a safe environment.
Finally, there is a reward system. KIRA provides virtual currency called Gems for learning activities. Users can use the Gems they earn to purchase items like beverages or desserts at the Gem Store. This connects learning with tangible rewards, making financial study a sustainable app-tech activity.
Mobile learning and gamification are the most natural forms of learning in the current era where smartphone proliferation is widespread. They offer many advantages, such as breaking down the temporal and spatial constraints of education and implementing a learner-centered educational environment. According to data from the Korean Financial Consumer Association, users who have experienced gamification in the financial field are positively affected in terms of learning motivation, immersion, and loyalty. This occurs because it stimulates intrinsic human motivations such as achievement, competition, reward, and social interaction. For example, Canada's financial education app Mydoh Play helps children learn difficult financial concepts like taxes and savings in a fun way through quizzes and mini-games.
The quality gap in financial education can be bridged with mobile platforms. As long as one has a smartphone, the same content is available anywhere. KIRA's Edu Fintech platform holds the potential to evolve beyond an educational tool into a data-driven personalized learning system. User quiz accuracy rates and simulated investment tendencies become valuable data. The system analyzes various data to identify which financial concepts users are weak in and provides tailored services to complement individual weaknesses.
South Korea has prepared to enhance the financial literacy of future generations. However, achieving the goal of "providing fair and effective financial education to the next generation" requires tools. By leveraging innovation and technology from the private sector in addition to policy design, South Korea is expected to advance as a financial powerhouse.
IT Donga Reporter Kang Hyung-seok (redbk@itdonga.com)
Various financial products such as savings, investments, loans, and pensions are flooding the market, providing more opportunities for asset formation through financial products. As such, understanding economic trends and financial products and efficiently managing assets have become crucial, emphasizing the importance of 'financial literacy'. Carmine DI NOIA, Director of Financial and Enterprise Affairs at the OECD, stated, "Although the use of digital financial services such as online shopping and mobile payments has increased, financial literacy remains low. Governments should provide age-appropriate financial experiences and ensure equal financial education for all students to reduce the gap." Financial literacy is seen as playing a key role beyond individual financial knowledge, affecting the effectiveness of monetary policy, economic growth, and financial stability.
The financial literacy of Korean citizens is on the decline. According to the Financial Supervisory Service's national financial literacy survey data released in 2024, the financial literacy score of Korean adults was 65.7, slightly down from 66.5 in 2022. Notably, the score for young adults in their 20s was 59.5 in the 'financial behavior' category, lower than the scores of 64.2 to 68.4 recorded by those in their 30s to 60s.
Advanced countries recognize the importance of financial education and reflect it in policies / Source=European Central Bank (ECB, Felix Schmidt)
The decline in financial literacy among elementary, middle, and high school students is also noteworthy. According to the 2024 economic literacy survey results for elementary, middle, and high school students announced by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance, sixth-grade elementary students scored 61.5, third-grade middle school students scored 51.9, and second-grade high school students scored 51.7. These scores represent declines of 3.9, 6.3, and 5.0 points, respectively, compared to 2022, with the exception of elementary students, failing to reach an average of 60 points. Analyzing the survey questions, the correct answer rates for practical life-related questions such as rational choice, e-commerce, and investment were high, but the rates for basic economic concepts and principles like inflation, supply and demand, and opportunity cost were low.
In the past, Koreans learned the financial structure through trial and error in society. They realize the need for financial education in the process of receiving wages, paying taxes, and taking loans. The problem is that the cost of trial and error is high. There are not a few cases where people lose assets accumulated over years due to wrong investment decisions or fall into excessive debt due to financial fraud.
However, financial education in Korea has just begun to take root. The Ministry of National Defense has decided to make economic education mandatory for military personnel starting in 2025, and the Ministry of Education will introduce a new subject on finance and economic life for second-year high school students in 2026. This contrasts with countries like the UK, the US, Japan, and Singapore, where public-private partnerships are conducting financial education for youth.
Advanced Countries Have Awakened to Financial Education
The UK is promoting financial education under the national goal of Financial Well-being. Since 2014, financial education has been integrated into the Personal, Social, Health, and Economic (PSHE) education curriculum. However, there are structural limitations in its implementation. PSHE is not a mandatory subject in all public schools, and financial education is selectively covered within the subject. Non-profit organizations have filled this gap in public education.
Financial education organizations such as My Bank and Money A+E operate tailored financial education programs for youth and adults. They secure funding through sponsorships from large financial institutions to ensure stable program operation. This is considered an exemplary case of how a public-private cooperation ecosystem can complement the limitations of public education.
Having experienced several financial crises, the US has reached a social consensus that individual financial soundness is directly linked to national economic stability. As a result, state governments have implemented strong policies requiring the completion of personal finance courses as a high school graduation requirement. As of 2024, 27 states are enforcing policies mandating the completion of finance courses.
Financially advanced countries provide systematic financial education for youth and adults / Source=National Debt Relief
US financial education focuses on practicality. It addresses real-world issues students will face immediately upon entering society, such as bank account management, the meaning of credit scores, student loans, and retirement preparation. The goal is not to produce economists but to cultivate financially independent citizens.
Japan significantly strengthened high school financial education in 2022, coinciding with the lowering of the adult age to 18. It teaches the characteristics of specific financial products such as stocks, bonds, and funds, and methods of asset formation, as well as national policies like the tax-free small investment system. In 2024, Japan established the Financial and Economic Education Promotion Organization (J-FLEC) with participation from the Financial Services Agency, the Bank of Japan, and private financial institutions. J-FLEC serves as the control tower overseeing national financial education.
Singapore's financial education focuses on integration. Although there is no separate financial subject, financial concepts are organically embedded throughout the curriculum. For example, budget management is taught during food and consumer education classes, while interest rates and taxes are covered in math classes. By incorporating financial concepts into the curriculum itself, it makes finance not a difficult academic subject but a basic life skill connected to all areas of life. Additionally, the Institute for Financial Literacy (IFL) provides financial education programs for the general public.
What About Financial Education in South Korea?
South Korea has also begun a major policy shift to enhance financial literacy among youth and young adults. The Ministry of National Defense will expand financial education for military personnel starting in 2025. This aims to prevent illegal sports gambling and excessive online payment behaviors as soldier salaries increase and smartphone use is permitted.
The Ministry of National Defense and the Financial Supervisory Service will expand the target of financial education from existing finance officers to all finance personnel, including non-commissioned officers and civilian employees. They plan to certify finance personnel as financial education instructors for military personnel, focusing on building internal education infrastructure. Financial education will address issues soldiers face in reality, such as asset management, voice phishing and cyber gambling prevention, understanding virtual assets, and pension planning.
The Ministry of Education will introduce a new elective subject on finance and economic life for second-year high school students starting in 2026, according to the revised curriculum. This subject will be reflected only in the school life record (admissions process) and not in the College Scholastic Ability Test, and will be an absolute evaluation subject. The finance and economic life subject consists of four courses: happy and safe financial life, income and expenditure, savings and investment, and credit and risk management, focusing on developing students' practical financial life skills.
Filling the Gap in Financial Education with Mobile and Gamification
The financial education policies of the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of National Defense are the foundation for future generations to enjoy a rational economic life. However, for financial education in South Korea to naturally expand, a digital financial education solution that is easily accessible to everyone is needed. To translate policy intentions into practical changes on the ground, educational tools and platforms that meet the future generation's expectations are necessary. Edu Fintech startup KIRA&Company proposes a solution that changes the paradigm of financial education by combining gamification and mobile learning (M-Learning).
The mobile Edu Fintech service KIRA is designed to naturally acquire financial knowledge / Source=IT Donga
The mobile Edu Fintech service KIRA is designed to naturally acquire financial knowledge through an organic financial education system that could otherwise be tedious and challenging.
First, KIRA provides basic financial knowledge, individual stocks and cryptocurrencies, and the latest economic issues in short and fun quiz formats to help anyone easily learn financial knowledge. It builds learning-related habits through micro-learning. The content, organized by securities analysts and experts from the UK accounting field, enhances its completeness.
Next, the knowledge gained through quizzes can be immediately applied in a virtual environment (simulated investment) linked to real market data. This approach resolves the gap between theory and practice by experiencing the principles of complex financial products in a safe environment.
Finally, there is a reward system. KIRA provides virtual currency called Gems for learning activities. Users can use the Gems they earn to purchase items like beverages or desserts at the Gem Store. This connects learning with tangible rewards, making financial study a sustainable app-tech activity.
The mobile Edu Fintech service KIRA provides a financial education platform suitable for the smartphone era / Source=IT Donga
Mobile learning and gamification are the most natural forms of learning in the current era where smartphone proliferation is widespread. They offer many advantages, such as breaking down the temporal and spatial constraints of education and implementing a learner-centered educational environment. According to data from the Korean Financial Consumer Association, users who have experienced gamification in the financial field are positively affected in terms of learning motivation, immersion, and loyalty. This occurs because it stimulates intrinsic human motivations such as achievement, competition, reward, and social interaction. For example, Canada's financial education app Mydoh Play helps children learn difficult financial concepts like taxes and savings in a fun way through quizzes and mini-games.
The quality gap in financial education can be bridged with mobile platforms. As long as one has a smartphone, the same content is available anywhere. KIRA's Edu Fintech platform holds the potential to evolve beyond an educational tool into a data-driven personalized learning system. User quiz accuracy rates and simulated investment tendencies become valuable data. The system analyzes various data to identify which financial concepts users are weak in and provides tailored services to complement individual weaknesses.
South Korea has prepared to enhance the financial literacy of future generations. However, achieving the goal of "providing fair and effective financial education to the next generation" requires tools. By leveraging innovation and technology from the private sector in addition to policy design, South Korea is expected to advance as a financial powerhouse.
IT Donga Reporter Kang Hyung-seok (redbk@itdonga.com)
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News