Medical / Clinical Research
"Weight-Loss Surgery Reduces Body Weight by 30%"
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2025.10.15
Head of Surgery at Seoul Medical Center, Han Sang-moon, a Specialist in Obesity Surgery
Reduces the capacity for food intake... Enables weight loss and chronic disease treatment
Over 90% of surgeries in Korea are 'sleeve gastrectomy'... Some rebound effect after obesity surgery
Covered by health insurance if conditions like fatty liver are present
Reduces the capacity for food intake... Enables weight loss and chronic disease treatment
Over 90% of surgeries in Korea are 'sleeve gastrectomy'... Some rebound effect after obesity surgery
Covered by health insurance if conditions like fatty liver are present
‘Why does the weight remain the same despite exercising and taking medication?’
While obesity treatments like Wegovy and Mounjaro are being released, these injectable drugs require continuous administration to maintain weight loss. The cost of the medication is significant, and side effects may occur. After achieving weight loss goals, the discontinuation rate of treatment is high.
On the other hand, bariatric surgery, which reduces the size of the stomach, helps the body continuously regulate weight on its own. It improves metabolism, reducing diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, making it a safe and effective treatment for severely obese patients. Health insurance coverage is also available. To understand what bariatric surgery is and who needs it, a detailed interview was conducted with Han Sang-moon, a bariatric surgery expert and chief of surgery at Seoul Medical Center.
―What is bariatric surgery, and what are its effects?
―What are the types of bariatric surgery?
―How is bariatric surgery conducted?
“Most surgeries are performed laparoscopically. There are about three or four scars, each about 1 to 2 cm, which are relatively small and disappear over time. Sleeve gastrectomy takes about 40 minutes to an hour, while gastric bypass surgery takes about 1 to 1 hour and 20 minutes. It takes about 3 to 4 days to be discharged. After about a week post-surgery, there is no hindrance to daily life.”
―What is the weight loss effect after bariatric surgery?
“Both gastrectomy and bypass surgery reduce the stomach size, resulting in immediate weight loss effects. Appetite significantly decreases from the day after surgery, and weight continues to decrease for 1 to 1.5 years. There is an initial weight loss effect of over 30% of the original weight. Afterward, it enters a maintenance phase. Bariatric surgery is an effective method for long-term weight management, lasting at least 5 to 10 years.”
―Does bariatric surgery also cause a yo-yo effect?
“Yes, the yo-yo effect can occur after bariatric surgery. The occurrence rate is about 10-15% for sleeve gastrectomy and 5-10% for gastric bypass surgery, which is much lower than with injections or oral medications. To minimize the yo-yo effect, it is important to regularly check health status. The yo-yo effect is often due to the quality rather than the quantity of food. For example, even if one eats less, consuming high-calorie foods is typical.”
―Are there any digestive function issues after bariatric surgery?
“After bariatric surgery, the stomach size decreases, reducing food intake, but the stomach slightly expands over time. In the early stages post-surgery, weight loss and fluid loss may lead to physical issues. Adequate protein supplementation is necessary to reduce physical limitations and ensure healthy weight loss. Mineral and vitamin intake is also recommended. After 1 to 2 years post-surgery, there are no significant digestive function issues. Sleeve gastrectomy allows for endoscopic examination of the stomach. However, for gastric bypass surgery, endoscopy is not easy, so the pre-surgery stomach condition and family history are checked.”
―Is bariatric surgery covered by health insurance?
“Since 2019, health insurance coverage is available. It applies to cases where the Body Mass Index (BMI) exceeds 35 kg/m², or is over 30 kg/m² with obesity-related diseases. Obesity-related diseases include diabetes, hypertension, vascular diseases, fatty liver, sleep apnea, asthma, and musculoskeletal disorders due to weight.”
While obesity treatments like Wegovy and Mounjaro are being released, these injectable drugs require continuous administration to maintain weight loss. The cost of the medication is significant, and side effects may occur. After achieving weight loss goals, the discontinuation rate of treatment is high.
On the other hand, bariatric surgery, which reduces the size of the stomach, helps the body continuously regulate weight on its own. It improves metabolism, reducing diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, making it a safe and effective treatment for severely obese patients. Health insurance coverage is also available. To understand what bariatric surgery is and who needs it, a detailed interview was conducted with Han Sang-moon, a bariatric surgery expert and chief of surgery at Seoul Medical Center.
―What is bariatric surgery, and what are its effects?
Getty Images Korea
“Bariatric surgery reduces the capacity of the stomach to hold food. When excessive weight gain occurs, various diseases often accompany it. However, bariatric surgery not only reduces weight but also positively changes body hormones, allowing for the treatment of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. In fact, many obese patients with diabetes have been able to reduce or stop their medication.”―What are the types of bariatric surgery?
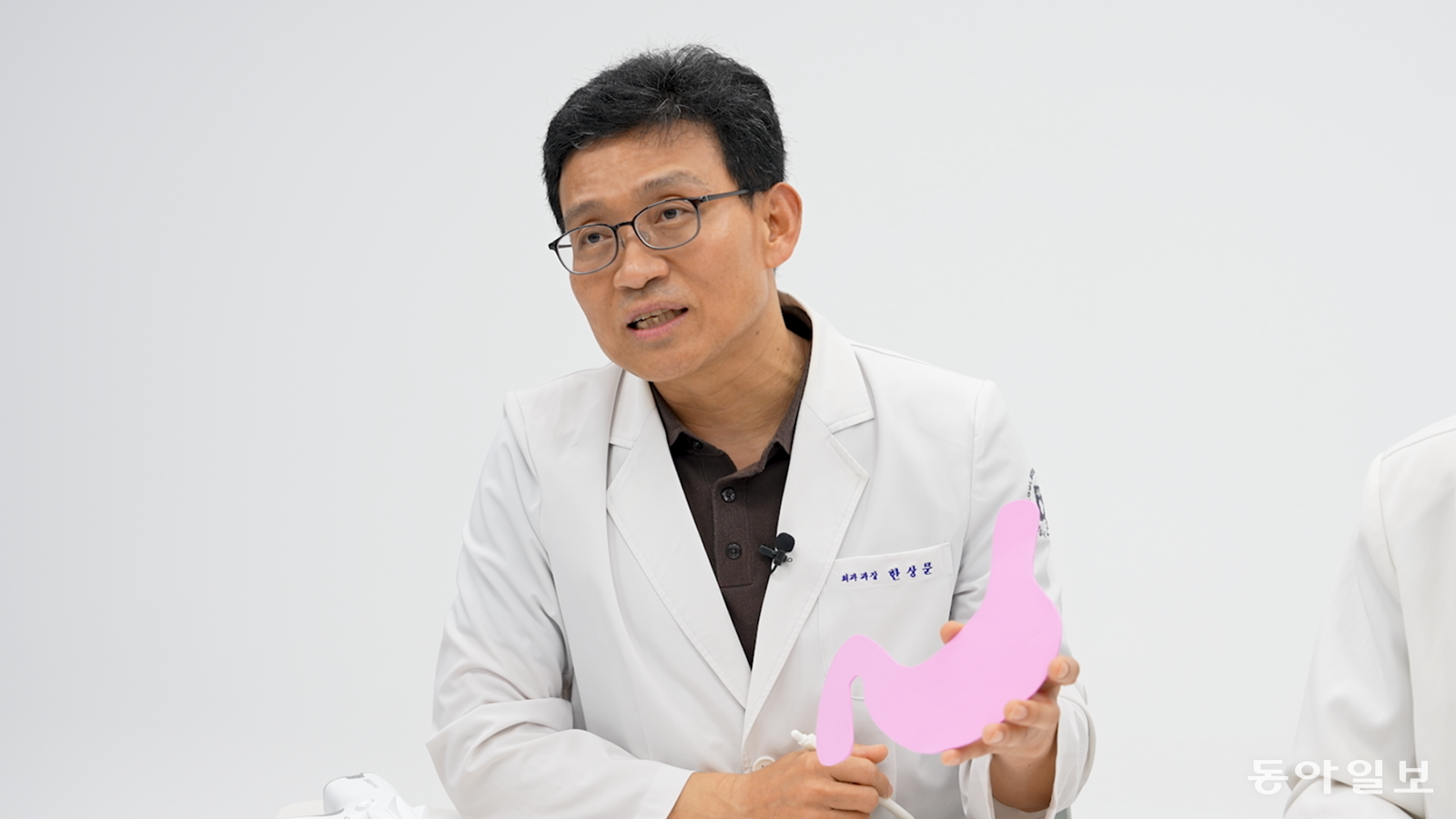
Han Sang-moon, a bariatric surgery expert and chief of surgery at Seoul Medical Center, explains the methods of bariatric surgery while holding a stomach model. Han stated, “Chronic disease patients can also treat diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia through bariatric surgery.” Lee Jin-han, medical journalist and doctor likeday@donga.com
“The most commonly performed surgery is sleeve gastrectomy. Simply put, it reduces the enlarged stomach to a banana shape, decreasing the amount of food intake. Globally, about 60% of bariatric surgeries, and over 90% in Korea, are sleeve gastrectomies. Another type is gastric bypass surgery, which separates the stomach and connects it directly to the small intestine. This reduces the amount of food entering the stomach and absorption, leading to weight loss. Although gastric bypass surgery is slightly more effective than gastrectomy, the surgical method should be determined based on the patient's individual characteristics. From a weight perspective, both surgeries are similar, but for diabetes treatment, bypass surgery is much more effective. People with obesity-related comorbidities without diabetes tend to undergo gastrectomy.”―How is bariatric surgery conducted?
“Most surgeries are performed laparoscopically. There are about three or four scars, each about 1 to 2 cm, which are relatively small and disappear over time. Sleeve gastrectomy takes about 40 minutes to an hour, while gastric bypass surgery takes about 1 to 1 hour and 20 minutes. It takes about 3 to 4 days to be discharged. After about a week post-surgery, there is no hindrance to daily life.”
―What is the weight loss effect after bariatric surgery?
“Both gastrectomy and bypass surgery reduce the stomach size, resulting in immediate weight loss effects. Appetite significantly decreases from the day after surgery, and weight continues to decrease for 1 to 1.5 years. There is an initial weight loss effect of over 30% of the original weight. Afterward, it enters a maintenance phase. Bariatric surgery is an effective method for long-term weight management, lasting at least 5 to 10 years.”
―Does bariatric surgery also cause a yo-yo effect?
“Yes, the yo-yo effect can occur after bariatric surgery. The occurrence rate is about 10-15% for sleeve gastrectomy and 5-10% for gastric bypass surgery, which is much lower than with injections or oral medications. To minimize the yo-yo effect, it is important to regularly check health status. The yo-yo effect is often due to the quality rather than the quantity of food. For example, even if one eats less, consuming high-calorie foods is typical.”
―Are there any digestive function issues after bariatric surgery?
“After bariatric surgery, the stomach size decreases, reducing food intake, but the stomach slightly expands over time. In the early stages post-surgery, weight loss and fluid loss may lead to physical issues. Adequate protein supplementation is necessary to reduce physical limitations and ensure healthy weight loss. Mineral and vitamin intake is also recommended. After 1 to 2 years post-surgery, there are no significant digestive function issues. Sleeve gastrectomy allows for endoscopic examination of the stomach. However, for gastric bypass surgery, endoscopy is not easy, so the pre-surgery stomach condition and family history are checked.”
―Is bariatric surgery covered by health insurance?
“Since 2019, health insurance coverage is available. It applies to cases where the Body Mass Index (BMI) exceeds 35 kg/m², or is over 30 kg/m² with obesity-related diseases. Obesity-related diseases include diabetes, hypertension, vascular diseases, fatty liver, sleep apnea, asthma, and musculoskeletal disorders due to weight.”
Lee Jin-han
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News