Hyundai
Hyundai Develops World-First Tech to Detect Blind-Spot Obstacles
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2026.01.30
Driving safety technology ‘Vision Pulse’ unveiled
UWB signals used to “see through” obstacles
“Determines position with an error margin under 10 cm”
UWB signals used to “see through” obstacles
“Determines position with an error margin under 10 cm”
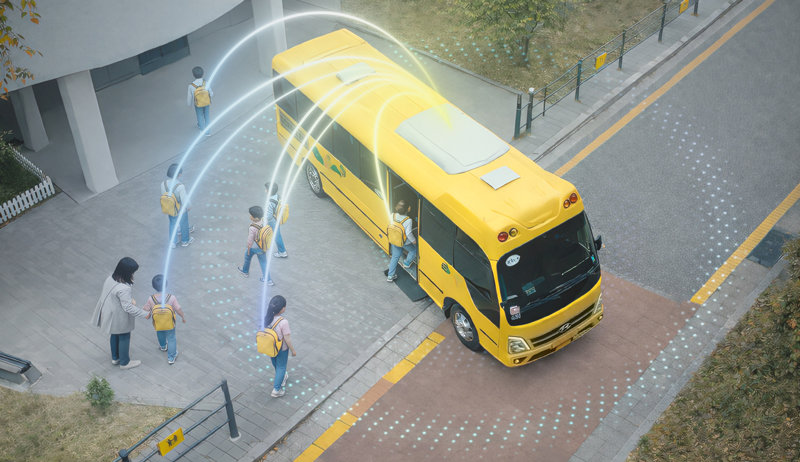
Concept image of Hyundai Motor Group’s blind-spot detection system “Vision Pulse.” Provided by Hyundai Motor Group
In the field of automotive safety, technology capable of detecting not only the vehicle directly ahead but also the movements of the vehicle in front of it in advance has long been a key challenge. With such technology, it would be possible to prevent multi-car collisions on highways and achieve breakthrough advances in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies. However, it has been difficult to realize this type of technology with current obstacle-detection sensors such as cameras and LiDAR.Hyundai Motor Group has now unveiled this blind-spot obstacle detection technology for the first time. Hyundai Motor and Kia announced on the 29th that they have developed “Vision Pulse,” a technology that uses radio waves to identify the positions of surrounding obstacles in real time to support safe driving, for the first time in the world.
Vision Pulse is a technology in which a radio-wave transmission device installed in the vehicle emits ultra-wideband (UWB) radio waves to detect obstacles. When UWB in the gigahertz (GHz) frequency band is emitted in all directions, it bypasses or penetrates obstacles and reaches those in blind spots, then relays this information back to the vehicle. Due to the characteristics of UWB, interference with other radio waves is minimal, and obstacles can be detected within 1–5 ms (milliseconds; 1 ms is one-thousandth of a second). The company explained, “It is highly precise, capable of identifying obstacles within a 100 m range with an error margin of less than 10 cm.”
In particular, for vehicles equipped with the “Digital Key 2” option, which allows the engine to be started with a smartphone, once Vision Pulse is commercialized, this function can be used without adding separate hardware, simply through a software update. For detection by this system, pedestrians and other vehicles must also carry or be equipped with a UWB transmission device, but as this does not entail significant cost, the technology is expected to spread rapidly. This is because UWB is already used in products for loss prevention and location tracking in the latest smartphones, such as Apple AirTag and Galaxy SmartTag.
Since last year, Hyundai Motor Group has been conducting a proof-of-concept project by applying this technology on a trial basis to forklifts operating on the production line at Kia’s Purpose-Built Vehicle (PBV) Conversion Center in Hwaseong, Gyeonggi Province, in order to prevent collisions between forklifts and workers. In October last year, the group also signed a business agreement with Busan Port Authority and plans to soon carry out a technology verification project to prevent collision accidents by applying this technology to industrial vehicles operating in Busan Port terminals and logistics hinterland sites.
A company official stated, “Vision Pulse is a technology that fully reflects our philosophy of putting safety first,” and added, “As it can be applied not only to the mobility industry but also across other sectors where safety is critical, it is expected to make a significant contribution to the safety of people and industry in the future.”
Lee Won-joo
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News