Tech / Autonomous Driving Sensors
Lambda Innovation Vision Aims to Lead FMCW LiDAR
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2026.01.23
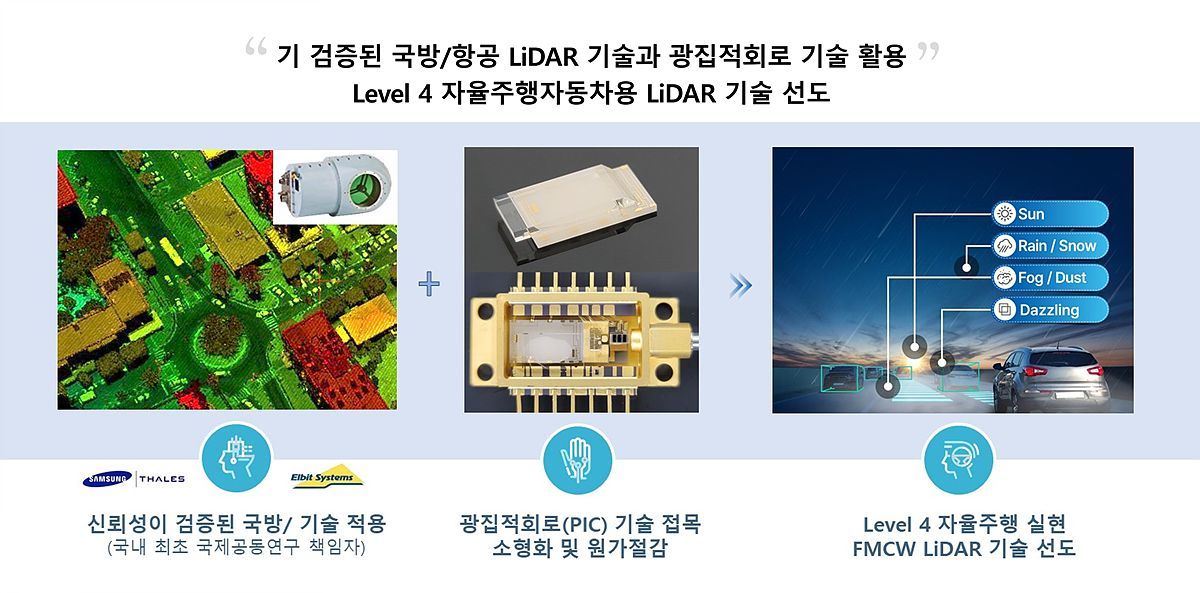
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, which measures distance with high precision using lasers, is drawing attention. Following applications in aerospace, metrology, and military equipment, it has recently been highlighted as a core technology for autonomous-driving mobility. Until now, “pulsed LiDAR,” which mainly uses high-speed pulses, has been widely used. This technology measures distance based on a simple and concise principle, but in conditions such as rain or fog, the laser is scattered and cannot fully demonstrate its capabilities.
In response, the industry points to Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) LiDAR as an alternative. This technology measures distance by precisely analyzing differences in the frequency of light. It operates with very high precision and blocks interference from rain, fog, and sunlight. It also has the advantage of being able to measure long distances even at low output power.
In fact, the aerospace industry has long been researching distance measurement technologies based on laser interference and phase. The concept of precise distance measurement using lasers was applied in the United States’ lunar exploration program, the Apollo Project, after which pulsed laser-based distance measurement technologies began to develop in earnest. However, technologies that precisely control laser frequency and utilize phase information were, due to limitations in laser, electronics, and signal-processing technologies at the time, used only in large, high-cost systems and did not spread across industries. Against this backdrop, Korean company LambdaInnoVision is taking the lead in miniaturizing and enhancing the performance of modern FMCW LiDAR and distributing it to industry, based on its long-accumulated precision laser control technology and the capabilities of its employees.
CEO Jongpil Ra of LambdaInnoVision researched LiDAR technology for a long period at a large corporation. He received the President’s Award from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) for developing Korea’s first laser Doppler vibrometer, and later received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, selected among the “Top 100 Excellent National R&D Achievements,” for developing an FMCW LiDAR system capable of penetrating smoke and securing visibility in disaster situations. Having developed Korea’s first defense LiDAR, he aims to bring to market FMCW LiDAR that combines performance and cost competitiveness by incorporating Photonic Integrated Circuit (PIC) technology.
Centered around CEO Ra, master’s and doctoral-level personnel who have researched core FMCW LiDAR technologies—such as geometrical and physical optics, lasers and FMCW signal processing, high-speed parallel computation, and PIC design and packaging—have joined the company. These individuals hold a total of 28 LiDAR-related patents (21 registered, 7 pending) in and outside Korea. As a result, LambdaInnoVision has secured the capability not only to independently cover the entire cycle of FMCW LiDAR—from component and system development to verification—but also to enhance performance while reducing unit costs.
The FMCW LiDAR developed by the company demonstrates many advantages. While pulsed LiDAR uses high-output lasers, FMCW LiDAR uses low-output continuous-wave lasers in the 1550 nm (nanometer) band. The wavelength of this laser does not reach the human retina. Therefore, when installed in autonomous-driving mobility solutions, it can be used safely even when pedestrians and drivers are mixed in close proximity.
Low-output continuous-wave lasers also demonstrate strong performance in environments with rain or snow, and in conditions with fog or smoke. Their inherent high transmittance and high signal-to-noise ratio deliver excellent detection performance. LambdaInnoVision further enhances this with coherent detection technology, which simultaneously utilizes frequency and phase information. This technology prevents reduced detection range or false detections caused by strong sunlight, ambient lighting, or the light sources of other LiDAR systems. CEO Ra emphasizes that FMCW LiDAR can detect extremely weak signals at the single-photon level, providing high reliability and predictability in aerospace and autonomous-driving fields.
Another advantage of LambdaInnoVision’s FMCW LiDAR is its ability to detect distance and speed information using the Doppler effect (the phenomenon where frequency changes when either the source or the observer is moving). When applying LiDAR to autonomous-driving mobility, it is necessary to precisely detect not only distance but also speed information. Since pulsed LiDAR cannot directly detect speed, it estimates speed by recognizing objects in 3D images and tracking them. This process consumes time and computational resources and introduces the possibility of errors.
By contrast, LambdaInnoVision’s FMCW LiDAR uses the Doppler effect to simultaneously detect distance and speed information at every point. This makes it easy to distinguish between moving and stationary objects, thereby improving object recognition performance in autonomous-driving mobility. It also offers higher resolution. Whereas pulsed LiDAR delivers resolutions on the order of several centimeters, FMCW LiDAR achieves resolutions from several millimeters down to several tens of nanometers. In practice, this advantage has led to the use of FMCW LiDAR in the precise fabrication of large-aperture optical systems for space applications.
On the strength of these advantages, LambdaInnoVision has achieved various milestones. It has independently developed core components such as frequency-modulated lasers and transceiver modules for FMCW LiDAR and has conducted multiple demonstrations. These include: ▲ a road damage and ground subsidence detection system for the container yard at Yeosu Gwangyang New Port ▲ joint development of a collision-avoidance sensor system for military helicopters ▲ joint research and technology verification with autonomous vehicle companies. Its work producing and validating FMCW LiDAR for satellite docking assistance in cooperation with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) also stands out. By applying FMCW LiDAR—which is superior to existing optical technologies—to inter-satellite docking, which requires extremely precise handling of speed and distance, the company has significantly improved efficiency. Based on its technological capabilities and demonstrated field performance, LambdaInnoVision has been recognized for the growth potential of its FMCW LiDAR technology and has attracted a pre-Series A investment of KRW 2 billion from the “Innovative Growth Materials, Parts and Equipment Fund” managed by Yuanta Investment.
Building on these achievements, CEO Ra and LambdaInnoVision are steadily addressing further challenges. First, they are tackling cost reduction and miniaturization, the biggest obstacles to the widespread adoption of FMCW LiDAR. Their key assets are in-house development and production capabilities for core FMCW LiDAR components such as photonic integrated circuits and laser transceiver modules. LambdaInnoVision plans to work with small and midsize foundry companies in Korea to overcome this challenge and, going a step further, to internalize the production of core components themselves.
Reliability verification, demanded by global industries seeking LiDAR solutions, is seen as an opportunity for LambdaInnoVision. The company already has extensive experience supplying FMCW LiDAR to the defense and aerospace sectors, passing numerous tests and verifications. It seeks to expand its activities by offering FMCW LiDAR that can operate smoothly over long periods in extreme environments with significant temperature changes and vibration. CEO Ra expects that, in this process, the company will naturally resolve the final challenge of bridging the gap between technology and market demand.
LambdaInnoVision aims to deploy FMCW LiDAR across multiple industrial and scientific domains. It plans to solidify its position in the already active fields of space, aviation, and industrial metrology, and to supply high-performance FMCW LiDAR to sectors with high implementation difficulty. Building on this track record, it will enter the autonomous-driving mobility market and establish itself as a specialized FMCW LiDAR company that delivers reliability, mass-producibility, and cost competitiveness.
CEO Ra stated, “We aim to deploy FMCW LiDAR across all areas of advanced industry and science, as well as space and aviation. By supplying LambdaInnoVision’s technology to all self-moving objects, including autonomous-driving mobility and robots, we will grow into a core technology provider for the global industrial ecosystem.”
IT Donga, Reporter Cha Joo-kyung (racingcar@itdonga.com)
In response, the industry points to Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) LiDAR as an alternative. This technology measures distance by precisely analyzing differences in the frequency of light. It operates with very high precision and blocks interference from rain, fog, and sunlight. It also has the advantage of being able to measure long distances even at low output power.
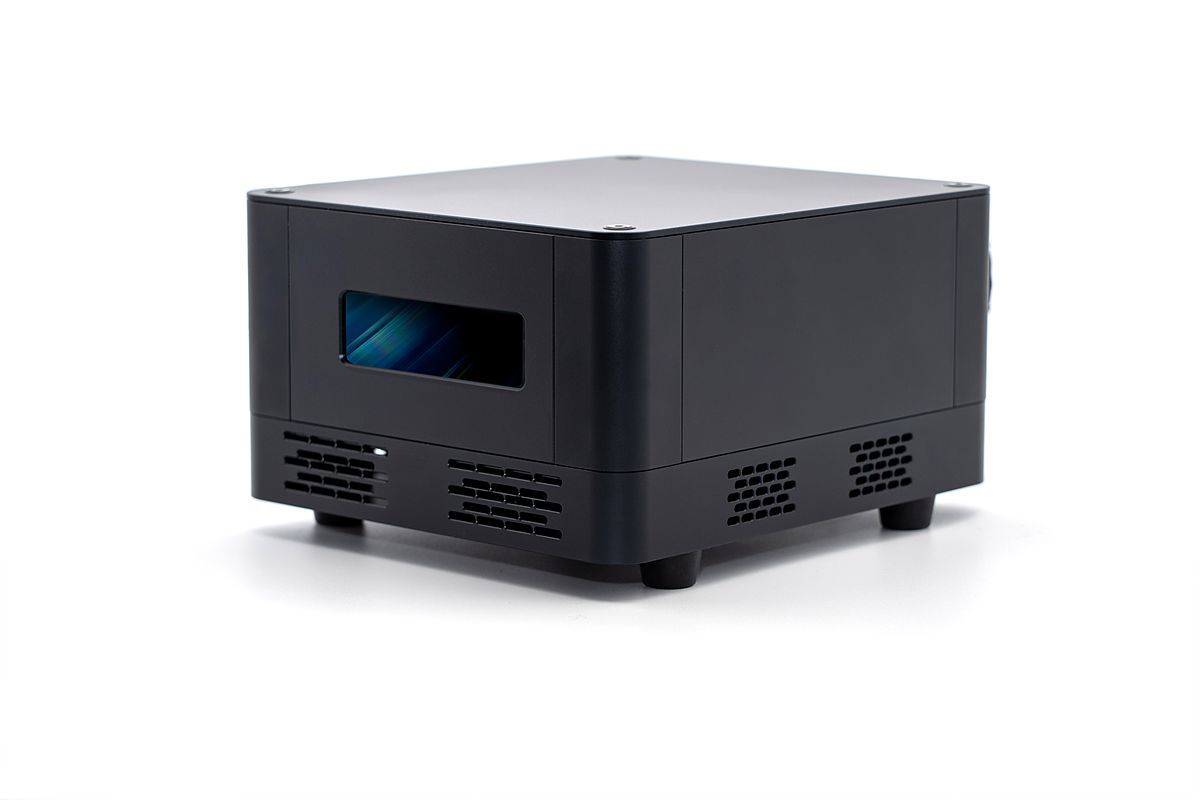
LambdaInnoVision’s FMCW LiDAR / Source = LambdaInnoVision
In fact, the aerospace industry has long been researching distance measurement technologies based on laser interference and phase. The concept of precise distance measurement using lasers was applied in the United States’ lunar exploration program, the Apollo Project, after which pulsed laser-based distance measurement technologies began to develop in earnest. However, technologies that precisely control laser frequency and utilize phase information were, due to limitations in laser, electronics, and signal-processing technologies at the time, used only in large, high-cost systems and did not spread across industries. Against this backdrop, Korean company LambdaInnoVision is taking the lead in miniaturizing and enhancing the performance of modern FMCW LiDAR and distributing it to industry, based on its long-accumulated precision laser control technology and the capabilities of its employees.
CEO Jongpil Ra of LambdaInnoVision researched LiDAR technology for a long period at a large corporation. He received the President’s Award from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) for developing Korea’s first laser Doppler vibrometer, and later received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, selected among the “Top 100 Excellent National R&D Achievements,” for developing an FMCW LiDAR system capable of penetrating smoke and securing visibility in disaster situations. Having developed Korea’s first defense LiDAR, he aims to bring to market FMCW LiDAR that combines performance and cost competitiveness by incorporating Photonic Integrated Circuit (PIC) technology.
Laser modules, essential components of LambdaInnoVision’s FMCW LiDAR, and their main applications / Source = LambdaInnoVision
Centered around CEO Ra, master’s and doctoral-level personnel who have researched core FMCW LiDAR technologies—such as geometrical and physical optics, lasers and FMCW signal processing, high-speed parallel computation, and PIC design and packaging—have joined the company. These individuals hold a total of 28 LiDAR-related patents (21 registered, 7 pending) in and outside Korea. As a result, LambdaInnoVision has secured the capability not only to independently cover the entire cycle of FMCW LiDAR—from component and system development to verification—but also to enhance performance while reducing unit costs.
The FMCW LiDAR developed by the company demonstrates many advantages. While pulsed LiDAR uses high-output lasers, FMCW LiDAR uses low-output continuous-wave lasers in the 1550 nm (nanometer) band. The wavelength of this laser does not reach the human retina. Therefore, when installed in autonomous-driving mobility solutions, it can be used safely even when pedestrians and drivers are mixed in close proximity.
LambdaInnoVision’s activity areas and key technologies / Source = LambdaInnoVision
Low-output continuous-wave lasers also demonstrate strong performance in environments with rain or snow, and in conditions with fog or smoke. Their inherent high transmittance and high signal-to-noise ratio deliver excellent detection performance. LambdaInnoVision further enhances this with coherent detection technology, which simultaneously utilizes frequency and phase information. This technology prevents reduced detection range or false detections caused by strong sunlight, ambient lighting, or the light sources of other LiDAR systems. CEO Ra emphasizes that FMCW LiDAR can detect extremely weak signals at the single-photon level, providing high reliability and predictability in aerospace and autonomous-driving fields.
Another advantage of LambdaInnoVision’s FMCW LiDAR is its ability to detect distance and speed information using the Doppler effect (the phenomenon where frequency changes when either the source or the observer is moving). When applying LiDAR to autonomous-driving mobility, it is necessary to precisely detect not only distance but also speed information. Since pulsed LiDAR cannot directly detect speed, it estimates speed by recognizing objects in 3D images and tracking them. This process consumes time and computational resources and introduces the possibility of errors.
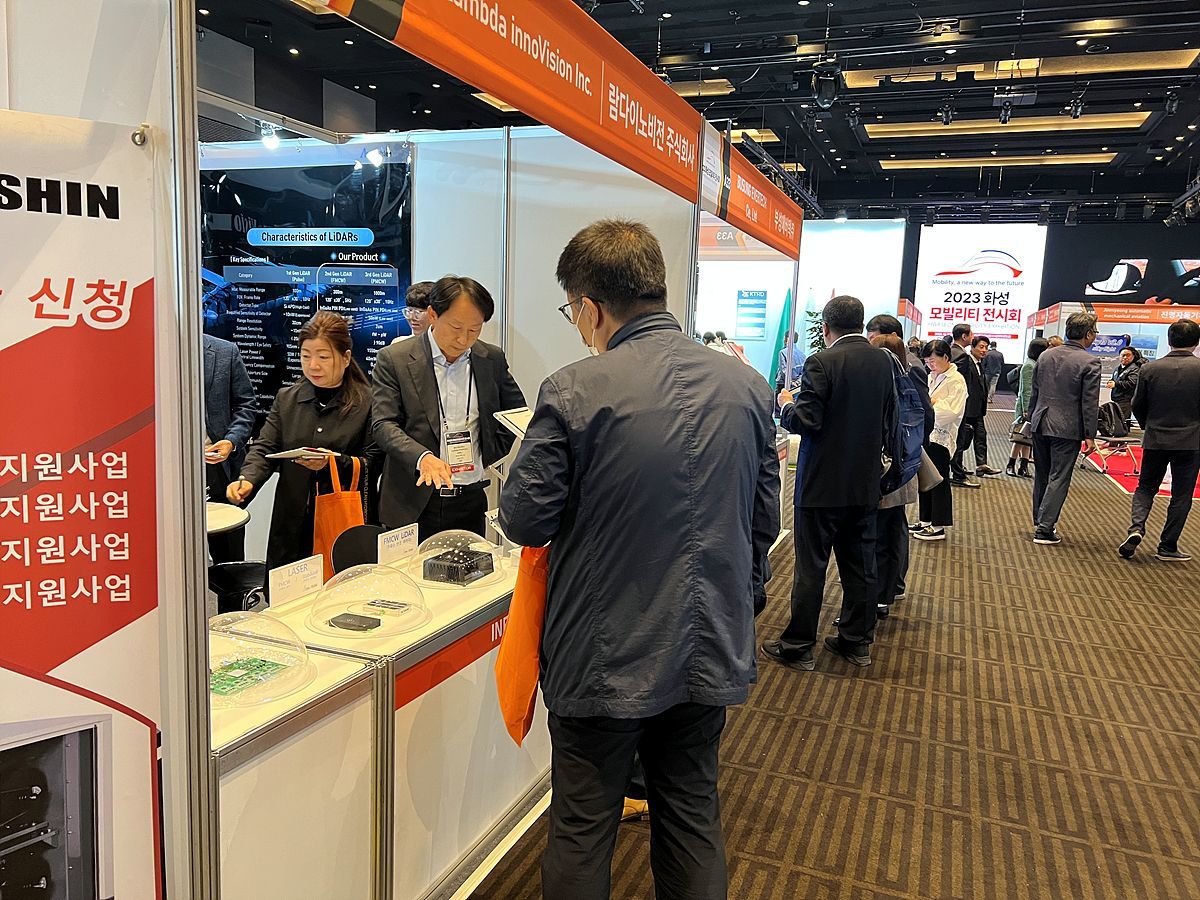
LambdaInnoVision presenting its technology at the 2023 Hwaseong Mobility Expo / Source = LambdaInnoVision
By contrast, LambdaInnoVision’s FMCW LiDAR uses the Doppler effect to simultaneously detect distance and speed information at every point. This makes it easy to distinguish between moving and stationary objects, thereby improving object recognition performance in autonomous-driving mobility. It also offers higher resolution. Whereas pulsed LiDAR delivers resolutions on the order of several centimeters, FMCW LiDAR achieves resolutions from several millimeters down to several tens of nanometers. In practice, this advantage has led to the use of FMCW LiDAR in the precise fabrication of large-aperture optical systems for space applications.
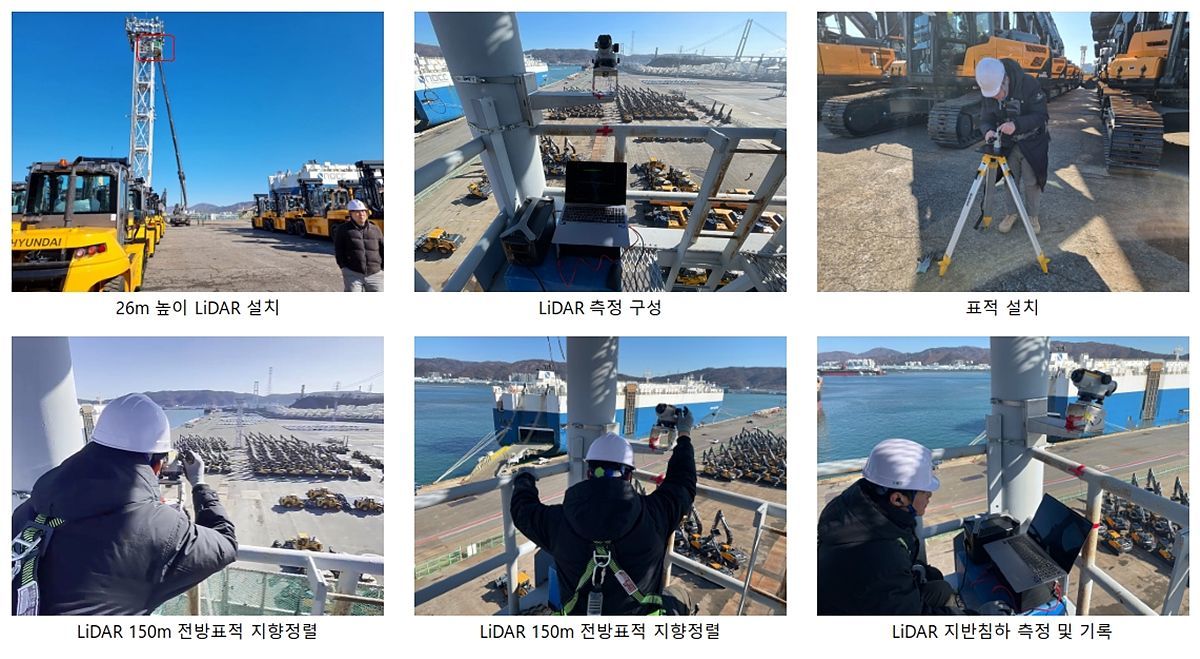
On the strength of these advantages, LambdaInnoVision has achieved various milestones. It has independently developed core components such as frequency-modulated lasers and transceiver modules for FMCW LiDAR and has conducted multiple demonstrations. These include: ▲ a road damage and ground subsidence detection system for the container yard at Yeosu Gwangyang New Port ▲ joint development of a collision-avoidance sensor system for military helicopters ▲ joint research and technology verification with autonomous vehicle companies. Its work producing and validating FMCW LiDAR for satellite docking assistance in cooperation with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) also stands out. By applying FMCW LiDAR—which is superior to existing optical technologies—to inter-satellite docking, which requires extremely precise handling of speed and distance, the company has significantly improved efficiency. Based on its technological capabilities and demonstrated field performance, LambdaInnoVision has been recognized for the growth potential of its FMCW LiDAR technology and has attracted a pre-Series A investment of KRW 2 billion from the “Innovative Growth Materials, Parts and Equipment Fund” managed by Yuanta Investment.
LambdaInnoVision demonstrating a LiDAR-based detection device for monitoring ground subsidence at a smart port / Source = LambdaInnoVision
Building on these achievements, CEO Ra and LambdaInnoVision are steadily addressing further challenges. First, they are tackling cost reduction and miniaturization, the biggest obstacles to the widespread adoption of FMCW LiDAR. Their key assets are in-house development and production capabilities for core FMCW LiDAR components such as photonic integrated circuits and laser transceiver modules. LambdaInnoVision plans to work with small and midsize foundry companies in Korea to overcome this challenge and, going a step further, to internalize the production of core components themselves.
Reliability verification, demanded by global industries seeking LiDAR solutions, is seen as an opportunity for LambdaInnoVision. The company already has extensive experience supplying FMCW LiDAR to the defense and aerospace sectors, passing numerous tests and verifications. It seeks to expand its activities by offering FMCW LiDAR that can operate smoothly over long periods in extreme environments with significant temperature changes and vibration. CEO Ra expects that, in this process, the company will naturally resolve the final challenge of bridging the gap between technology and market demand.
CEO Jongpil Ra introducing core components of FMCW LiDAR / Source = LambdaInnoVision
LambdaInnoVision aims to deploy FMCW LiDAR across multiple industrial and scientific domains. It plans to solidify its position in the already active fields of space, aviation, and industrial metrology, and to supply high-performance FMCW LiDAR to sectors with high implementation difficulty. Building on this track record, it will enter the autonomous-driving mobility market and establish itself as a specialized FMCW LiDAR company that delivers reliability, mass-producibility, and cost competitiveness.
CEO Ra stated, “We aim to deploy FMCW LiDAR across all areas of advanced industry and science, as well as space and aviation. By supplying LambdaInnoVision’s technology to all self-moving objects, including autonomous-driving mobility and robots, we will grow into a core technology provider for the global industrial ecosystem.”
IT Donga, Reporter Cha Joo-kyung (racingcar@itdonga.com)
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News