Business / Startup Support
Gwangju Center to Nurture Deep-Tech Unicorns
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2025.12.30
[Creative Economy Innovation Center Council x IT Donga] The Creative Economy Innovation Center Council, a national consultative body of Creative Economy Innovation Centers, has published the “Regional Startup Ecosystem Report” together with the Science and Technology Policy Institute, introducing the current status of startup ecosystems in major Korean cities and the activities of the Creative Economy Innovation Centers. IT Donga presents the Regional Startup Ecosystem Report in cooperation with the Creative Economy Innovation Center Council.
The “City of Light” Gwangju is shedding light on the future of Korea’s artificial intelligence (AI) and deep tech industries. By integrating an AI foundation into existing industries, providing full-scale support for deep tech research and development, and building a startup ecosystem in which talent, technology, and companies grow together, the city has completed the foundation for such progress.
The Creative Economy Innovation Center Council introduces Gwangju as both a “startup growth hub for connectivity and agglomeration” and an “AI industry convergence innovation hub.” Gwangju hosts major deep tech industrial zones such as the AI Convergence District, the Future-Oriented Automotive Industry District, and the Smart Energy Industry District. Universities and research/startup support institutions clustered in these areas have created a startup ecosystem that encompasses research and development, industry–academia collaboration, technology commercialization, and investment.
This startup ecosystem is being further advanced by Gwangju Metropolitan City and startup support institutions including the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation. Gwangju previously declared itself a “city of opportunity with a high startup success rate” and established three major strategic pillars—investment, infrastructure, and talent development—to build an innovative startup ecosystem. It then created a “Startup Valley” near Gwangju Station, and within it secured key resources to provide abundant, stage-specific support for companies: ▲ “Idea Factory,” which offers education and startup assistance for prospective founders ▲ “Bitgoeul Startup Station (Stage),” which drives the growth of startup companies ▲ “Complex Hub Center,” which strengthens the R&D capabilities of companies in the growth stage ▲ “Corporate Innovation Growth Center,” which supports full-scale scale-up ▲ “Urban Industrial Land,” which supports exit strategies such as IPOs and M&A as well as global expansion.
The Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation actively supports Gwangju Metropolitan City’s startup ecosystem strategy. Having operated for more than 10 years as a startup hub and public accelerator, the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation was selected as the first TIPS (Tech Incubator Program for Startup) operator in the Honam region, adding investment attraction and global expansion support to its full-cycle startup programs. The smartization of manufacturing and AI integration is led by Gwangju Technopark, while convergence innovation between cultural content and information and communication technology is spearheaded by the Gwangju Information & Culture Industry Promotion Agency.
The Creative Economy Innovation Center Council then introduces Gwangju’s AI industry convergence innovation hub. With the goal of “emerging as one of the world’s four leading AI powers,” Gwangju began building an AI complex in 2020, which has been in operation since July 2024. This has resulted in the establishment of advanced R&D infrastructure including ▲ an AI Data Center ▲ an AI Demonstration Startup Building ▲ a large-scale AI Driving Simulation facility.
Companies, research institutes, universities, and public institutions that move into this district are leveraging the AI R&D infrastructure to accelerate their growth. They receive support not only in terms of research infrastructure but also technology and talent. In particular, AI startups and pre-unicorn startups are provided with a variety of data center services. In addition, by 2030 Gwangju plans to establish ▲ a National AI Computing Center ▲ an AI Knowledge Industry Center ▲ an AI Innospace ▲ an AI Gifted High School. Once completed, Gwangju is expected to serve both as an industrial convergence innovation hub for an AI demonstration city and as a hub for the convergence of AI and manufacturing.
Among these initiatives, the Creative Economy Innovation Center Council recommends particular attention to the medihealthcare sector. Korea is a global leader in advanced medical technology, and the convergence of this strength with AI is expected to have significant impact. Gwangju is home to multiple medihealthcare research institutions, including Chonnam National University Hospital, the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Chosun University Hospital, and the Jeonnam Bioindustry Foundation. Related laboratories, companies, and support organizations have also taken root. Centered on the Gwangju Technopark Medihealthcare Center, they have built a robust network encompassing industry, academia, research institutes, hospitals, and other institutions. Based on this, they have drawn up a blueprint to expand the AI medihealthcare industrial base and to establish an innovation-driven growth system grounded in K-medical capabilities.
Gwangju’s strategy as a startup growth hub for connectivity and agglomeration, and as an AI industry convergence innovation hub, has already borne fruit. Findings from the Creative Economy Innovation Center Council’s survey attest to this. Since 2020, Gwangju’s startup ecosystem and its participants have steadily grown. As of 2024, universities’ technology transfer volume and related income amounted to 414 cases and KRW 525.3 billion, respectively. Venture investment over the same period reached KRW 87.2 billion, more than doubling compared with 2021 three years earlier.
The performance of the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation is even more notable. The size of its equity investment funds expanded from KRW 1.24 billion at the time of formation in 2021 to KRW 8.19 billion by 2025. Based on this, it has supported 26 startups, and the number of companies selected for TIPS rose from 6 in 2021 to 20 in 2024.
Unsurprisingly, the morale of ecosystem participants continues to improve. In a survey conducted by the Creative Economy Innovation Center Council among officials of companies headquartered in or active in Gwangju, 82.1% of respondents gave positive evaluations of Gwangju’s startup ecosystem. High scores were recorded across the board, including for the activities of startup support organizations (5.5 points out of 7), startup support programs run by local governments (5.15 points), and infrastructure including startup spaces (5.31 points). Eight out of ten companies indicated their intention to continue growing in Gwangju.
Building on this well-developed foundation and strong performance, Gwangju is evolving into a new form of startup ecosystem. It is aggregating talent from universities and research institutions into the state-led AI industrial base and demonstration support infrastructure. It is establishing an open collaborative framework among SMEs, mid-sized companies, large corporations, and startups, while upgrading startup education. Regional venture funds and public-led investment structures are also being more tightly woven. The Gwangju–Jeonnam startup cluster to be formed under the themes of connectivity, openness, transformation, innovation, and convergence is expected to become a place where AI demonstration infrastructure, talent, and regional linkage strategies are in balance.
Kim Dong-cheol, Director at the Gwangju–Jeonnam Regional Office of SMEs and Startups, said, “Gwangju is evolving into a startup city centered on technological innovation. Based on its AI infrastructure, it has built an environment that can drive innovation across various industries, including renewable energy, automotive robotics, and mobility. In particular, the city possesses an ecosystem that organically connects technology, talent, companies, and demonstration activities through the AI complex, data center, and Bitgoeul Startup Station. Gwangju will establish a full-cycle support system for startups as Korea’s AI-centric city.”
Lee Gwan-hee, Director at the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation, added, “Gwangju is emerging as an AI-centric city that integrates AI into future growth industries. The structure that combines regional research capabilities and infrastructure to support startups from founding through to global expansion is Gwangju’s strength and competitive edge. By discovering deep tech startups and validating markets through an investment-based approach, we aim to nurture region-based unicorn startups, and to become an institution that leads open innovation with large and mid-sized corporations and supports the pioneering of new global markets.”
Reporter Cha Ju-kyung, IT Donga (racingcar@itdonga.com)
The “City of Light” Gwangju is shedding light on the future of Korea’s artificial intelligence (AI) and deep tech industries. By integrating an AI foundation into existing industries, providing full-scale support for deep tech research and development, and building a startup ecosystem in which talent, technology, and companies grow together, the city has completed the foundation for such progress.
The Creative Economy Innovation Center Council introduces Gwangju as both a “startup growth hub for connectivity and agglomeration” and an “AI industry convergence innovation hub.” Gwangju hosts major deep tech industrial zones such as the AI Convergence District, the Future-Oriented Automotive Industry District, and the Smart Energy Industry District. Universities and research/startup support institutions clustered in these areas have created a startup ecosystem that encompasses research and development, industry–academia collaboration, technology commercialization, and investment.
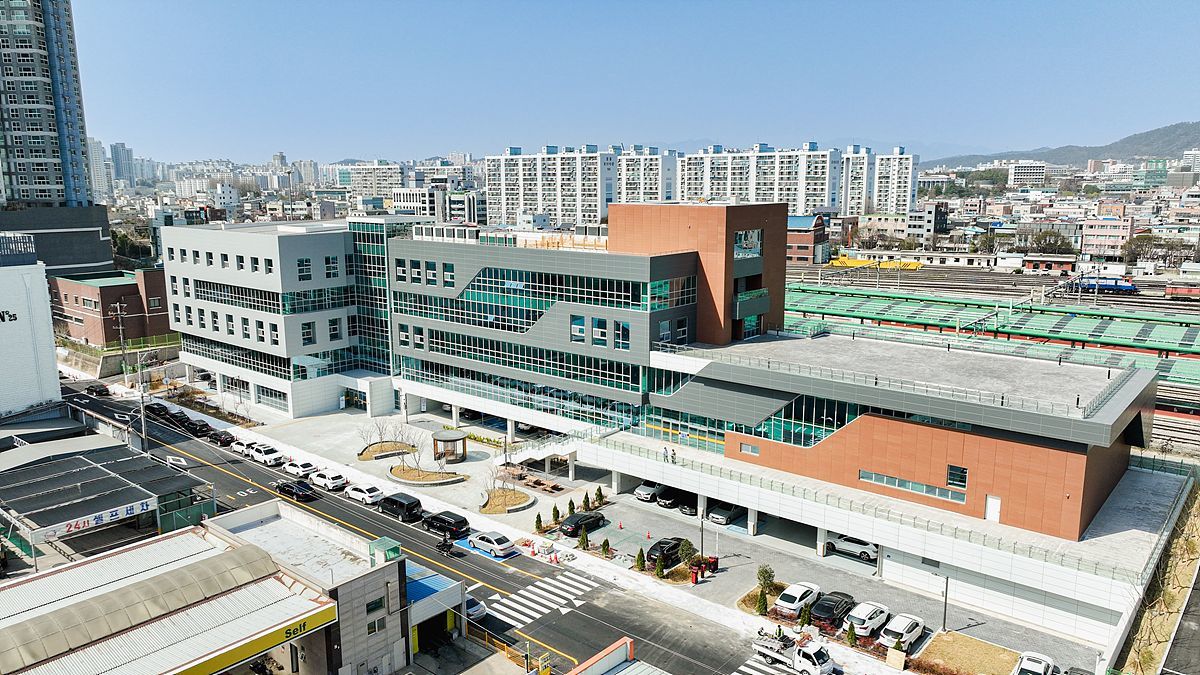
View of the Bitgoeul Startup Station (Stage) / Source = Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation
This startup ecosystem is being further advanced by Gwangju Metropolitan City and startup support institutions including the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation. Gwangju previously declared itself a “city of opportunity with a high startup success rate” and established three major strategic pillars—investment, infrastructure, and talent development—to build an innovative startup ecosystem. It then created a “Startup Valley” near Gwangju Station, and within it secured key resources to provide abundant, stage-specific support for companies: ▲ “Idea Factory,” which offers education and startup assistance for prospective founders ▲ “Bitgoeul Startup Station (Stage),” which drives the growth of startup companies ▲ “Complex Hub Center,” which strengthens the R&D capabilities of companies in the growth stage ▲ “Corporate Innovation Growth Center,” which supports full-scale scale-up ▲ “Urban Industrial Land,” which supports exit strategies such as IPOs and M&A as well as global expansion.
The Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation actively supports Gwangju Metropolitan City’s startup ecosystem strategy. Having operated for more than 10 years as a startup hub and public accelerator, the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation was selected as the first TIPS (Tech Incubator Program for Startup) operator in the Honam region, adding investment attraction and global expansion support to its full-cycle startup programs. The smartization of manufacturing and AI integration is led by Gwangju Technopark, while convergence innovation between cultural content and information and communication technology is spearheaded by the Gwangju Information & Culture Industry Promotion Agency.
Scene from the Gwangju Startup Festival / Source = Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation
The Creative Economy Innovation Center Council then introduces Gwangju’s AI industry convergence innovation hub. With the goal of “emerging as one of the world’s four leading AI powers,” Gwangju began building an AI complex in 2020, which has been in operation since July 2024. This has resulted in the establishment of advanced R&D infrastructure including ▲ an AI Data Center ▲ an AI Demonstration Startup Building ▲ a large-scale AI Driving Simulation facility.
Companies, research institutes, universities, and public institutions that move into this district are leveraging the AI R&D infrastructure to accelerate their growth. They receive support not only in terms of research infrastructure but also technology and talent. In particular, AI startups and pre-unicorn startups are provided with a variety of data center services. In addition, by 2030 Gwangju plans to establish ▲ a National AI Computing Center ▲ an AI Knowledge Industry Center ▲ an AI Innospace ▲ an AI Gifted High School. Once completed, Gwangju is expected to serve both as an industrial convergence innovation hub for an AI demonstration city and as a hub for the convergence of AI and manufacturing.
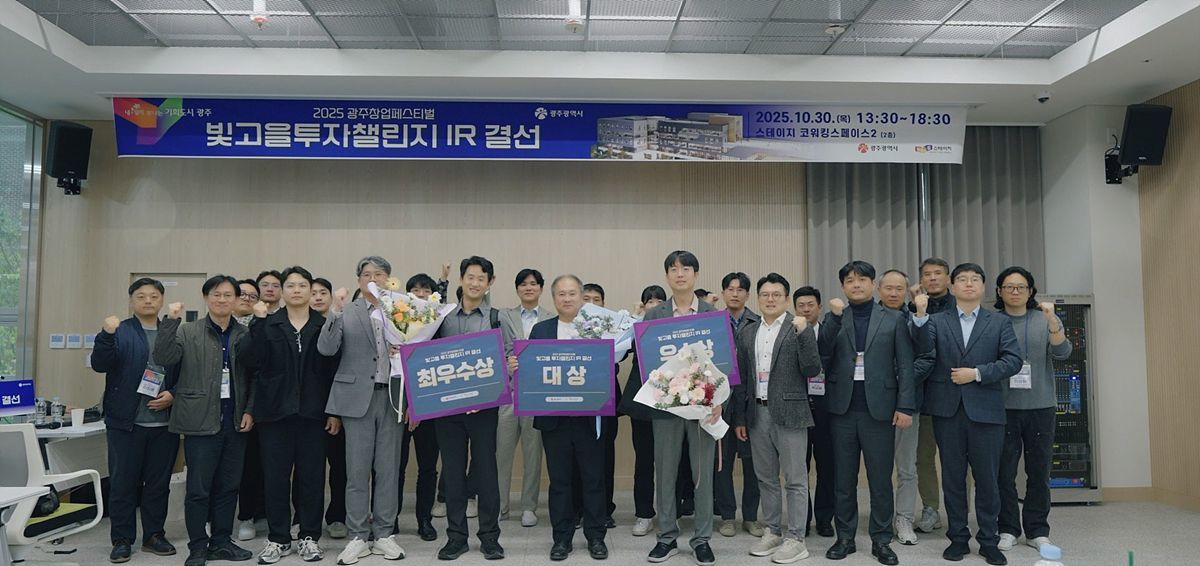
Scene from the Bitgoeul Investment Challenge / Source = Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation
Among these initiatives, the Creative Economy Innovation Center Council recommends particular attention to the medihealthcare sector. Korea is a global leader in advanced medical technology, and the convergence of this strength with AI is expected to have significant impact. Gwangju is home to multiple medihealthcare research institutions, including Chonnam National University Hospital, the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Chosun University Hospital, and the Jeonnam Bioindustry Foundation. Related laboratories, companies, and support organizations have also taken root. Centered on the Gwangju Technopark Medihealthcare Center, they have built a robust network encompassing industry, academia, research institutes, hospitals, and other institutions. Based on this, they have drawn up a blueprint to expand the AI medihealthcare industrial base and to establish an innovation-driven growth system grounded in K-medical capabilities.
Gwangju’s strategy as a startup growth hub for connectivity and agglomeration, and as an AI industry convergence innovation hub, has already borne fruit. Findings from the Creative Economy Innovation Center Council’s survey attest to this. Since 2020, Gwangju’s startup ecosystem and its participants have steadily grown. As of 2024, universities’ technology transfer volume and related income amounted to 414 cases and KRW 525.3 billion, respectively. Venture investment over the same period reached KRW 87.2 billion, more than doubling compared with 2021 three years earlier.
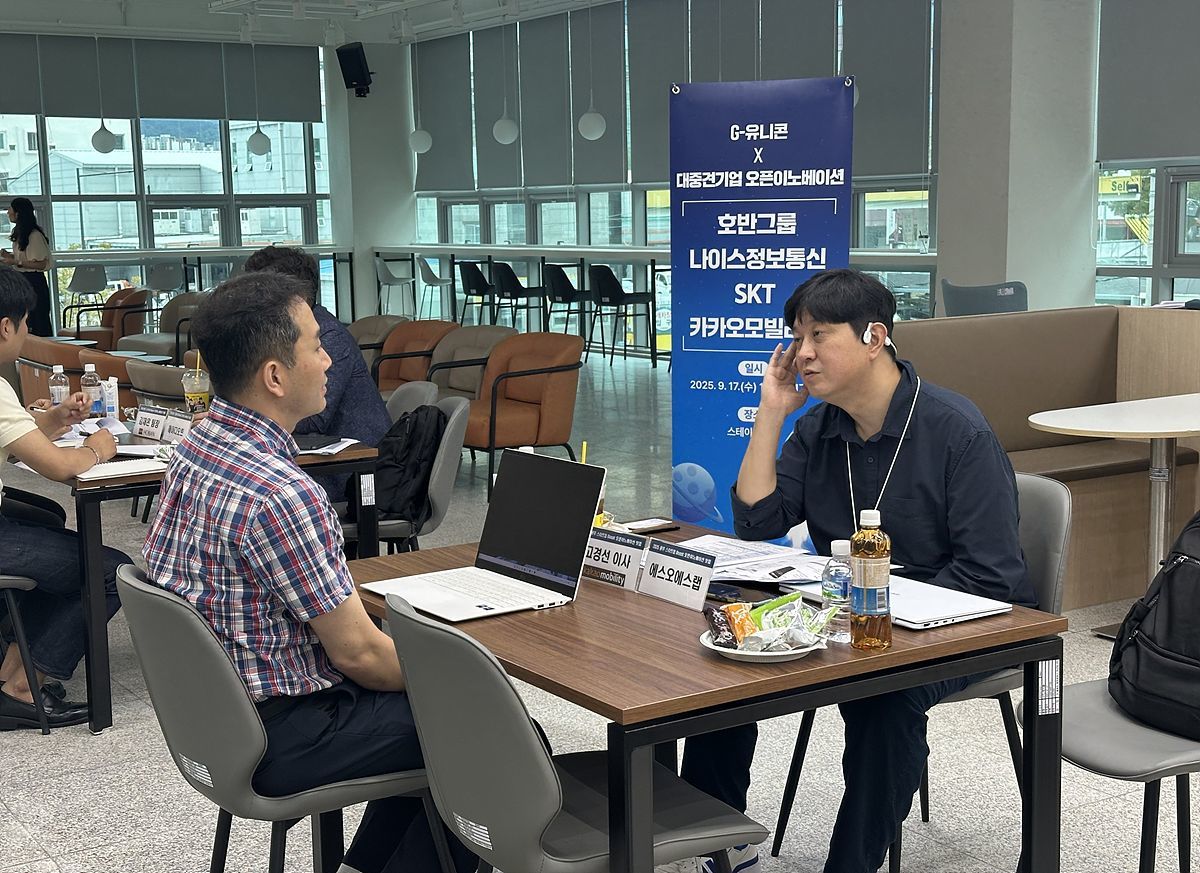
Scene from the Unicorn Open Innovation event / Source = Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation
The performance of the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation is even more notable. The size of its equity investment funds expanded from KRW 1.24 billion at the time of formation in 2021 to KRW 8.19 billion by 2025. Based on this, it has supported 26 startups, and the number of companies selected for TIPS rose from 6 in 2021 to 20 in 2024.
Unsurprisingly, the morale of ecosystem participants continues to improve. In a survey conducted by the Creative Economy Innovation Center Council among officials of companies headquartered in or active in Gwangju, 82.1% of respondents gave positive evaluations of Gwangju’s startup ecosystem. High scores were recorded across the board, including for the activities of startup support organizations (5.5 points out of 7), startup support programs run by local governments (5.15 points), and infrastructure including startup spaces (5.31 points). Eight out of ten companies indicated their intention to continue growing in Gwangju.
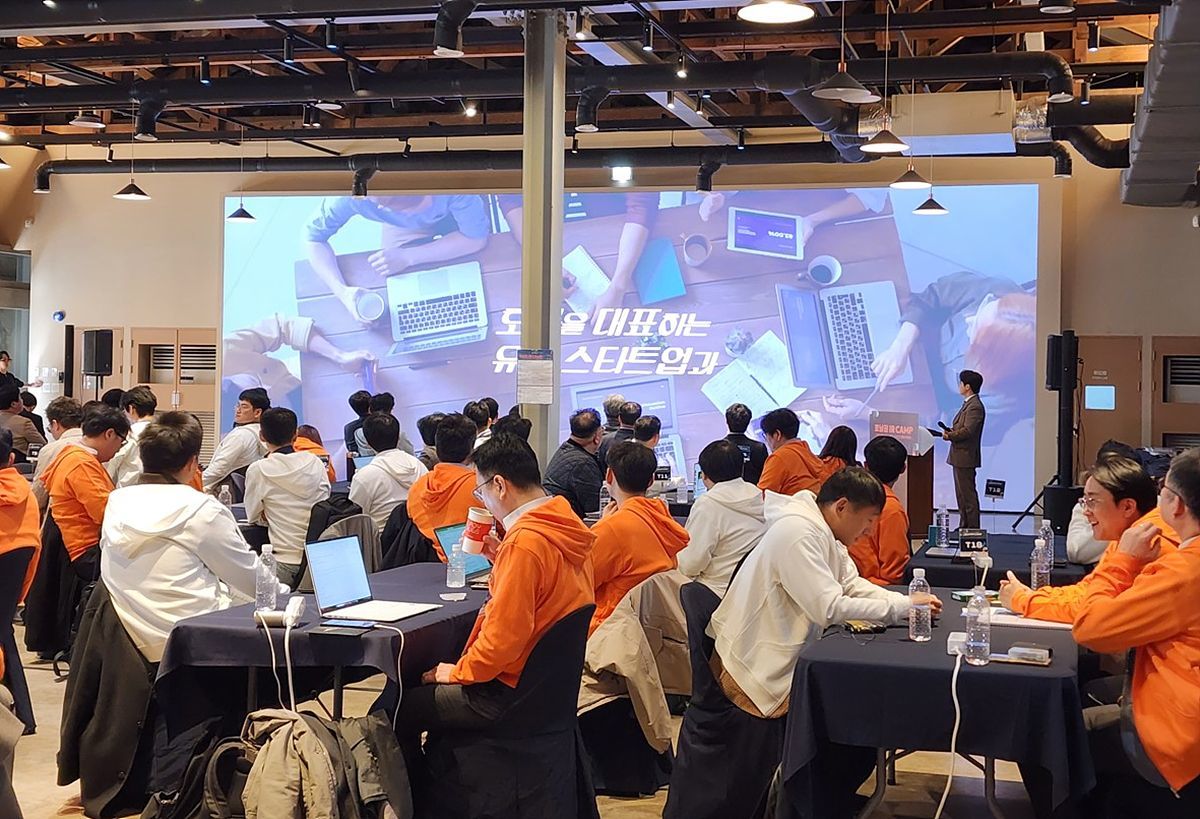
Scene from the Integrated IR Camp / Source = Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation
Building on this well-developed foundation and strong performance, Gwangju is evolving into a new form of startup ecosystem. It is aggregating talent from universities and research institutions into the state-led AI industrial base and demonstration support infrastructure. It is establishing an open collaborative framework among SMEs, mid-sized companies, large corporations, and startups, while upgrading startup education. Regional venture funds and public-led investment structures are also being more tightly woven. The Gwangju–Jeonnam startup cluster to be formed under the themes of connectivity, openness, transformation, innovation, and convergence is expected to become a place where AI demonstration infrastructure, talent, and regional linkage strategies are in balance.
Kim Dong-cheol, Director at the Gwangju–Jeonnam Regional Office of SMEs and Startups, said, “Gwangju is evolving into a startup city centered on technological innovation. Based on its AI infrastructure, it has built an environment that can drive innovation across various industries, including renewable energy, automotive robotics, and mobility. In particular, the city possesses an ecosystem that organically connects technology, talent, companies, and demonstration activities through the AI complex, data center, and Bitgoeul Startup Station. Gwangju will establish a full-cycle support system for startups as Korea’s AI-centric city.”
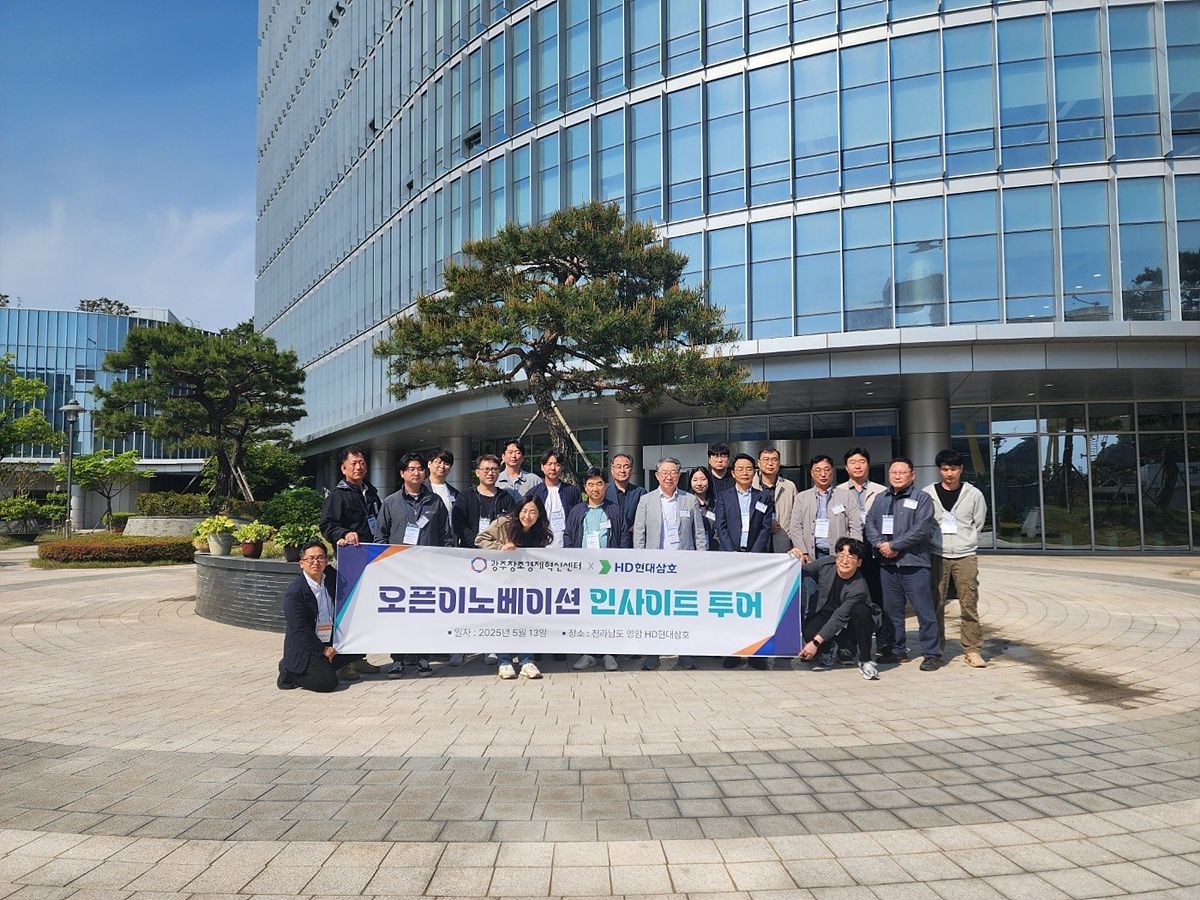
Scene from participation in Hyundai Samho Open Innovation / Source = Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation
Lee Gwan-hee, Director at the Gwangju Center for Creative Economy & Innovation, added, “Gwangju is emerging as an AI-centric city that integrates AI into future growth industries. The structure that combines regional research capabilities and infrastructure to support startups from founding through to global expansion is Gwangju’s strength and competitive edge. By discovering deep tech startups and validating markets through an investment-based approach, we aim to nurture region-based unicorn startups, and to become an institution that leads open innovation with large and mid-sized corporations and supports the pioneering of new global markets.”
Reporter Cha Ju-kyung, IT Donga (racingcar@itdonga.com)
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News