MedTech
Simple blood test detects cancer earlier
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2026.01.14
Misconceptions and Facts About Liquid Biopsy
Applied to monitoring and recurrence prediction…potential to transform the paradigm of early diagnosis
Most accurate when combined with tissue biopsy…cost of KRW 400,000–2,000,000 remains a burden
Applied to monitoring and recurrence prediction…potential to transform the paradigm of early diagnosis
Most accurate when combined with tissue biopsy…cost of KRW 400,000–2,000,000 remains a burden
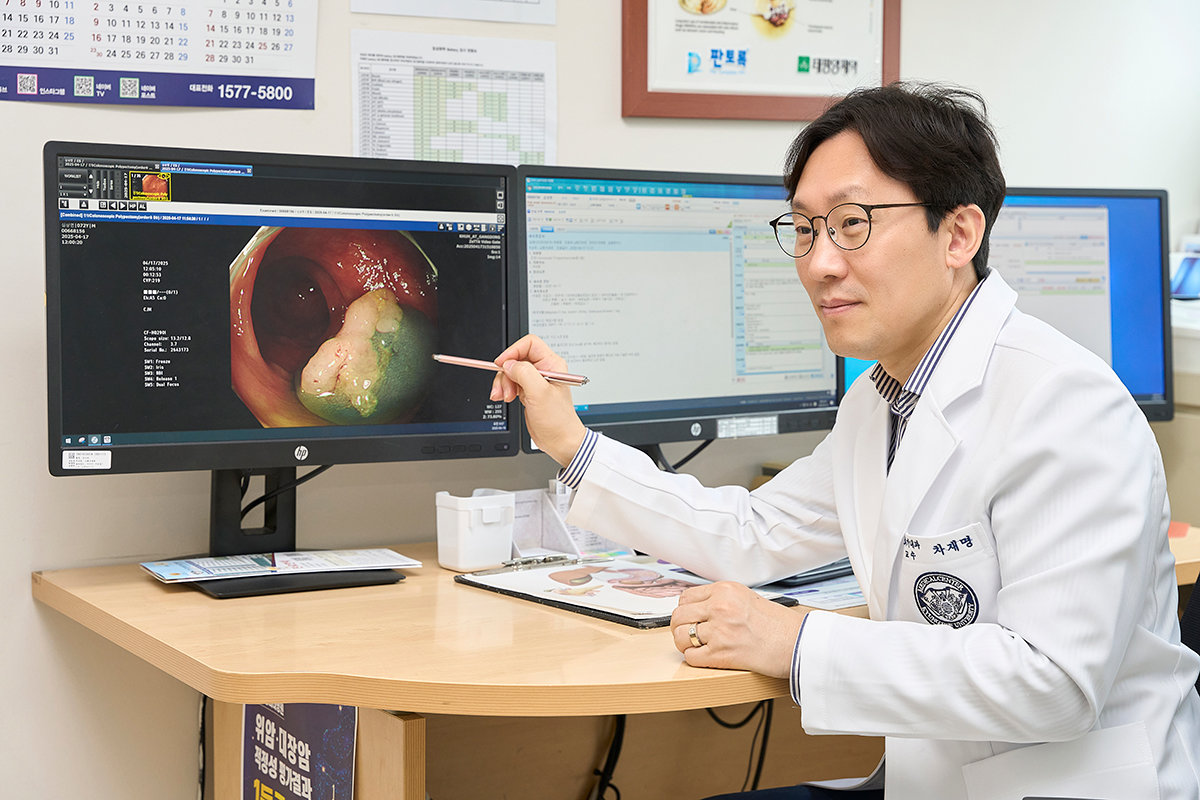
Cha Jae-myung, Director of the Health Promotion Center at Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, forecasts a shift from tissue biopsy, which diagnoses cancer through tissue sampling, to liquid biopsy, which can diagnose cancer through blood tests. He also expects that liquid biopsy technology will be applied not only to cancer but also to the early diagnosis and monitoring of other serious diseases such as neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases. Courtesy of Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong
When hospitals refer to a biopsy, people typically think of a method in which a sharp needle is inserted into a suspicious area to collect tissue for examination if cancer is suspected. The most common example is a tissue biopsy performed when thyroid cancer is suspected. Recently, however, liquid biopsy, a method that determines the presence of cancer through a simple blood test instead of a biopsy of the suspicious area, has been gaining attention.Cha Jae-myung, Director of the Health Promotion Center at Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, explained, “Unlike conventional tissue biopsy, which is an invasive method that physically removes tumor tissue, liquid biopsy detects and analyzes specific components of cancer, such as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), circulating tumor cells, and exosomes, which are substances derived from cancer cells, through a simple blood draw.” He emphasized, “This technology is being widely used, not only for early cancer diagnosis but also for treatment monitoring in advanced cancer and for surveillance of minimal residual disease (MRD) to predict postoperative recurrence.” In an interview with Director Cha, he discussed myths and facts about liquid biopsy in detail.
– Recently, interest in liquid biopsy in health checkups has increased.
“The main reason liquid biopsy technology is drawing attention is its potential to transform the paradigm of early cancer diagnosis. Regular blood tests have had limitations in checking for cancer onset because of the burden associated with tissue sampling. The earlier cancer is detected, the more dramatically survival rates increase, so the value of liquid biopsy, which is simple and repeatable, is very high. It has the advantage of reflecting tumor heterogeneity at the time of testing and enabling monitoring of minimal residual disease. Even if cancer has spread to multiple sites in the body, liquid biopsy can identify its genetic information at once and detect even extremely small traces of residual cancer cells remaining in the blood after surgery. This means it can predict recurrence risk at an early stage and enable preemptive treatment. It is believed that an era is opening in which cancer screening will be possible with a single blood draw.”
– What indicators can be identified through liquid biopsy?
“Liquid biopsy provides in-depth information on the molecular characteristics of cancer through analysis of circulating tumor nucleic acids (ctDNA). This helps increase the precision of diagnosis and treatment. First, it can precisely analyze mutations or structural alterations in specific genes related to cancer development and growth, such as cancer-specific gene mutations (EGFR, KRAS, TP53). These findings can be used to select targeted anticancer therapies tailored to the individual. Second, unlike normal cells, cancer cells exhibit abnormal changes at the initiation site of tumor suppressor gene expression, known as DNA methylation changes. DNA methylation alterations occur widely from the very early stages of carcinogenesis. Therefore, analyzing such cancer-specific methylation patterns in ctDNA can be useful for early cancer screening. In other words, by analyzing mutations in cancer cells, test results can serve as indicators from the initial onset of cancer through to the selection of therapeutic agents.”
– How reliable are liquid biopsy results?
“The reliability of liquid biopsy depends on the clinical objective. For genetic mutation analysis in advanced cancer and monitoring of minimal residual disease to predict recurrence after early-stage cancer surgery, the amount of ctDNA in the blood is relatively sufficient, and high reliability has been recognized. It has already become established as a standard test method in clinical practice and is covered by the National Health Insurance. In the area of early cancer diagnosis, liquid biopsy has also demonstrated superior clinical performance to existing cancer screening tests, such as fecal occult blood testing in early colorectal cancer screening, and has already been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is reimbursed by health insurance. In the field of gastric cancer, it has been approved in some countries, including China. It also shows high clinical accuracy in various cancers, including breast, lung, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers. Although screening for cancers other than colorectal cancer and a few others is not yet approved, there is a high possibility that FDA and other regulatory approvals will be obtained for these cancers within the next few years.”
– What are the limitations of liquid biopsy?
“At present, when the number of cancer cells is extremely small, or when changes occur in normal cells, they may be mistaken for cancer cells. In other words, there are situations where non-cancer cases are misinterpreted as cancer, or cancer cases are misinterpreted as non-cancer. However, the technology is advancing rapidly, and these issues are expected to be overcome soon.”
– Can liquid biopsy replace existing cancer screening?
“No. Liquid biopsy is a testing method that supplements the shortcomings of existing screening and lowers the barrier to early detection. Although it has an advantage over conventional tissue biopsy in genomic analysis of advanced cancer and in minimal residual disease surveillance, at present, even when liquid biopsy results are positive, the most accurate and safe approach is to link them with standard examinations such as imaging tests or tissue biopsy for final confirmation. Costs also vary. Tests for individual cancers range from the KRW 400,000 level to the KRW 1,000,000 level, and when tests that include assessment of risk for various diseases are added, they can reach the KRW 2,000,000 level. It is advisable to select tests in consultation with hospital-level medical professionals.”
– How is liquid biopsy expected to develop going forward?
“Liquid biopsy technology will evolve toward increasing precision at every stage of cancer diagnosis and treatment. In particular, ultra-high-sensitivity, personalized testing technologies specialized for MRD surveillance to predict postoperative recurrence are expected to be standardized, enabling preemptive treatment for patients at high risk of recurrence. In addition, AI-based integrated diagnostics are expected to improve the accuracy of early detection and more precisely predict the timing of treatment response and resistance. Research will also actively progress on expanding the application of liquid biopsy technology beyond cancer to the early diagnosis and monitoring of other serious diseases, such as neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases.”
Lee Jin-han
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News