Investment Trend
SpaceX IPO Hopes Signal Private Space Big Bang
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2026.01.02
First space company IPO set for the second half of this year
KRW 43 trillion funding secured for first Mars exploration plan
Blue Origin, Rocket Lab and others expand operations
Space data center market also expected to grow
KRW 43 trillion funding secured for first Mars exploration plan
Blue Origin, Rocket Lab and others expand operations
Space data center market also expected to grow
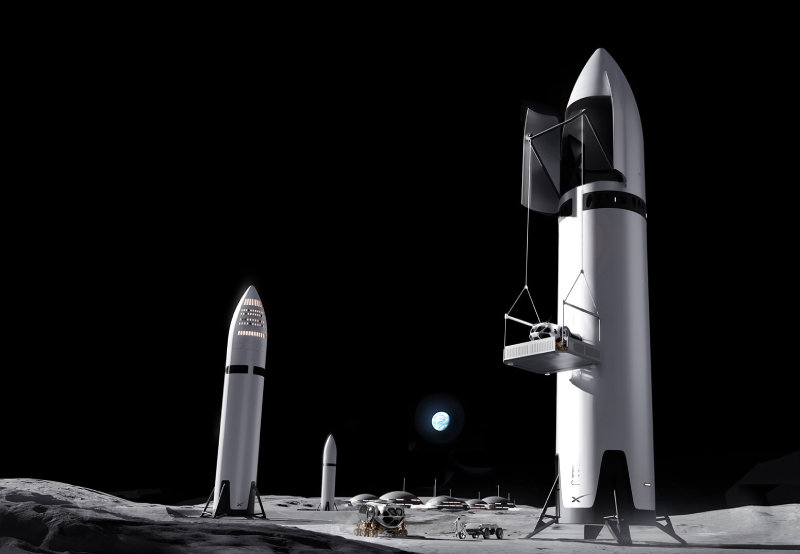
An imagined future lunar landing scene released by SpaceX. Astronauts who reach the Moon aboard the approximately 120-meter-tall Starship will be able to ride an elevator down to the lunar surface. SpaceX has stated that it also plans to build a lunar base where astronauts can live in the future. Provided by SpaceX.
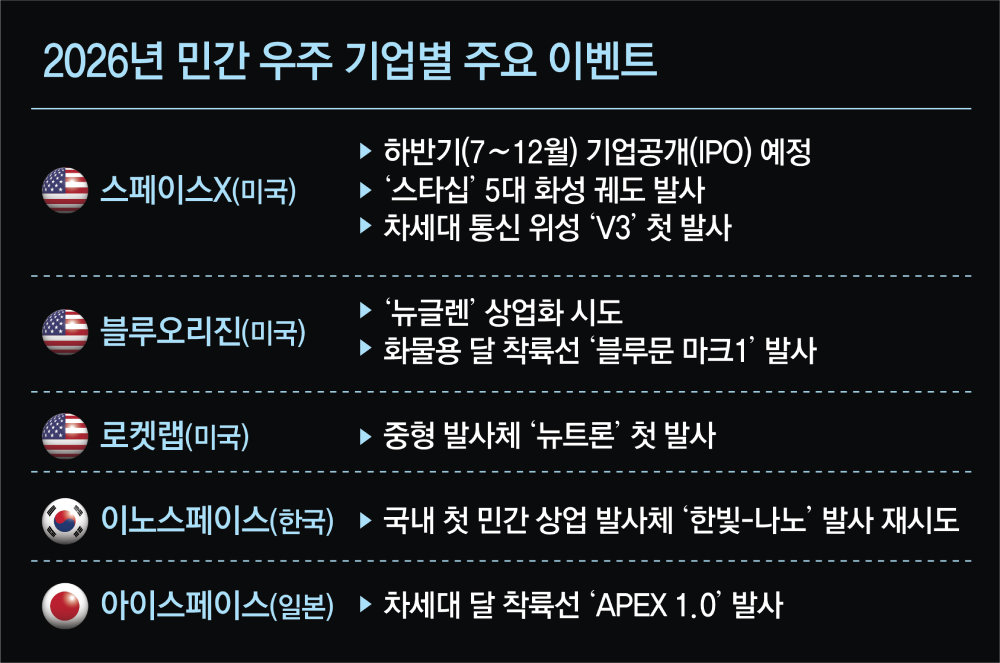
The global space company SpaceX is preparing for an initial public offering (IPO) in the second half of this year (July–December), and expectations are emerging that this year will mark an explosive expansion of the private space market. It suggests that the space industry’s “ChatGPT moment” (the advent of ChatGPT that led to the mass adoption of AI), in which satellite launches and related activities become popularized, is just around the corner.According to the aerospace industry on the 1st, SpaceX plans to raise about USD 30 billion (approximately KRW 43.41 trillion) through what would be the largest-ever IPO in the second half of this year. Once the first large-scale listing of a space company is realized, institutional investors are also expected to jump in, opening a full-fledged “space economy” in the new year. Mark Boggett, CEO of venture capital firm Seraphim Space, said in an interview with MarketWatch that “this year’s SpaceX IPO will be an event capable of triggering tectonic shifts across the entire space economy.”
New capital is already flowing in, as share prices of space startups such as Rocket Lab and Firefly Aerospace have risen sharply in recent days. As investor expectations grow, private companies are preparing to move beyond mere technology demonstrations into full-scale operations.
● Musk to attempt first Mars exploration
Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla and founder of SpaceX.
SpaceX plans to use the capital secured through the IPO to undertake its first Mars exploration mission this year. Elon Musk, Tesla CEO and founder of SpaceX, has said that the company aims to send five Starships at the end of this year, when the orbits of Earth and Mars are at their closest. Since this window recurs only once every 26 months, SpaceX intends to make maximum use of this opportunity. Starship is the largest launch vehicle in human history and can carry around 100 astronauts.Not only in the United States but also in Japan and Korea, companies are entering the space transport market this year, including Japan’s ispace and Korea’s Innospace. Innospace became the first Korean private company to attempt a commercial launch this year, but the attempt failed due to vehicle damage. The company plans to make a second launch attempt in the first half of this year (January–June).
● Space data center market to grow to KRW 56 trillion by 2035
The expansion of the space economy is also expected to extend to “space data centers.” As power supply issues driven by artificial intelligence (AI) intensify, space data centers offer advantages such as no need for land or cooling costs and the ability to save power by using solar energy. Data centers can be operated at roughly 10% of the cost required on the ground. Market research firm Research and Markets forecasts that the space data center market will grow from USD 176.70 million (approximately KRW 2.571 trillion) in 2029 to USD 3.90905 billion (approximately KRW 56.564 trillion) in 2035.
SpaceX has stated that it plans to expand its next-generation “V3” satellites used for its Starlink satellite communication service for data center applications in the future. V3 satellites have data transmission capabilities of 1 terabit per second (a speed that transmits 1 trillion bits of data per second), and their first launch is scheduled for this year.
U.S. startup StarCloud launched the space data center “StarCloud-1” last year. In October this year, it plans to launch “StarCloud-2,” equipped with Nvidia graphics processing units (GPUs) such as the H100 and B200.
Choi Ji-won
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News