Medical / Research
Daewoong Pharmaceutical Hosts 4D Symposium on Personalized Diabetes Care
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2025.12.23
Daewoong 4D Symposium establishes itself as a platform for treatment strategy discussion
66 endocrinologists participated this year
Discussing tailored therapies for high‑risk patients including SGLT-2 inhibitors
Presenting precision diagnosis and management strategies using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)
66 endocrinologists participated this year
Discussing tailored therapies for high‑risk patients including SGLT-2 inhibitors
Presenting precision diagnosis and management strategies using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)
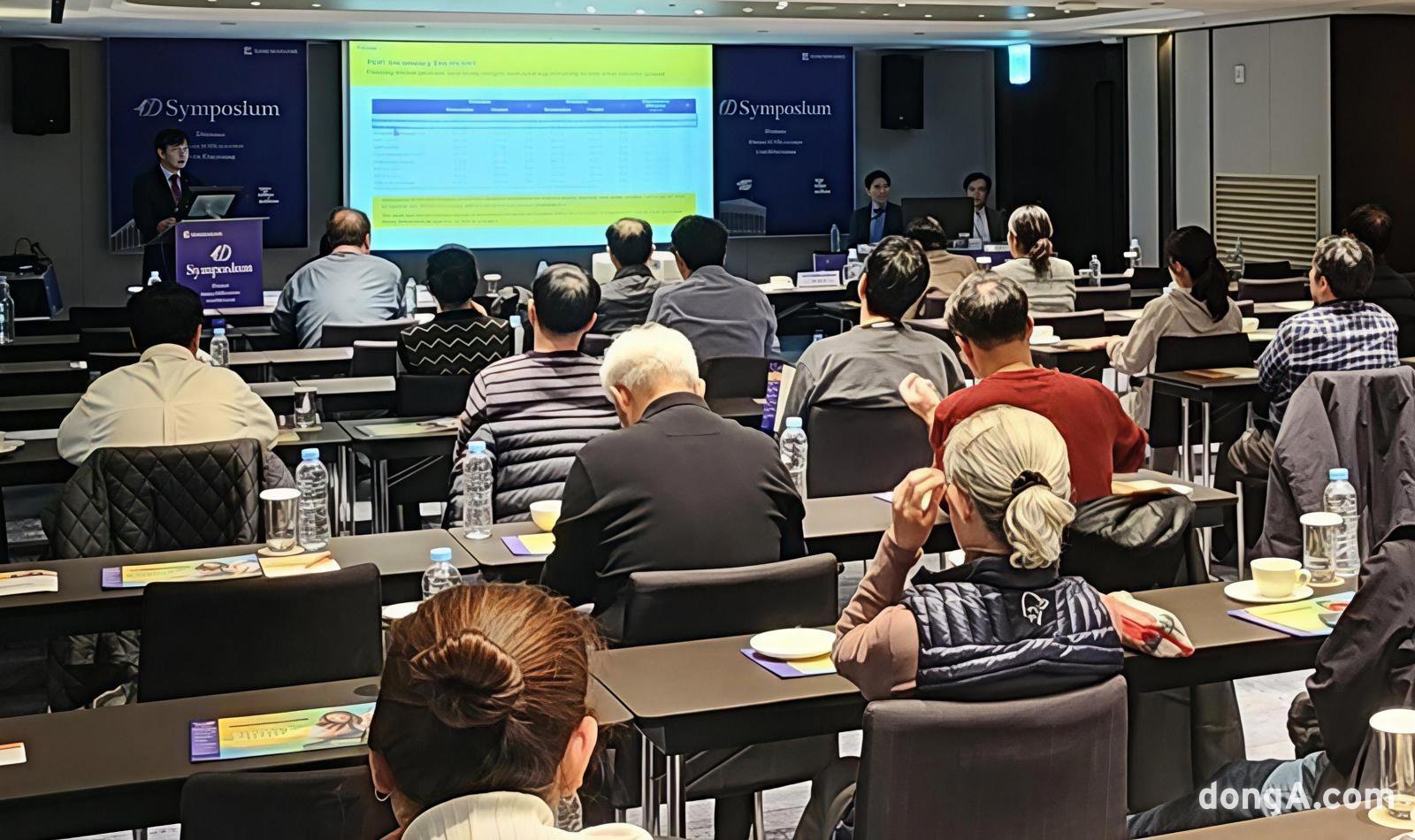
Panoramic view of Daewoong Pharmaceutical’s 4D Symposium
Daewoong Pharmaceutical announced on the 23rd that it discussed initial treatment strategies and criteria for drug selection in relation to this year’s revised diabetes treatment guidelines through its academic program “4D Symposium (Diabetes Debate & Discussion symposium with Daewoong),” which is joined by endocrinologists.The Daewoong 4D Symposium, now in its fifth year, is characterized by its focus on panel discussions and Q&A sessions rather than lecture-style, didactic academic events. Professors from university hospitals and community-based physicians participated together to share the latest evidence and real-world clinical experience, and to enable more practical discussion of problems frequently encountered in daily practice.
This event was held over two days with the participation of 66 endocrinology specialists including university hospital professors and community practitioners. Leading domestic experts in diabetes, including Professors Sung-Rae Kim, Shin-Gon Kim, Young-Min Cho, and In-Kyung Jeong, served as chairs and led the main sessions.
Professor Young-Min Cho of Seoul National University College of Medicine speaks at Daewoong Pharmaceutical’s 4D Symposium.
Revised treatment guidelines present treatment strategies tailored to high-risk groups
In this program, medical staff focused on how to apply the revised diabetes treatment guidelines to actual prescribing. Treatment guidelines serve as a reference standard for physicians when initiating therapy and selecting medications. In the latest revision, the emphasis was strengthened on setting treatment priorities by considering not only blood glucose levels but also the risk of major complications such as cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and kidney disease, along with the patient’s overall condition. Accordingly, discussion centered on prioritizing SGLT-2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists for high-risk groups, while continuing to regard metformin as an important treatment option for the general patient population.SGLT-2 inhibitors are diabetes treatments that lower blood glucose by reducing renal glucose reabsorption and increasing urinary glucose excretion. They can help with weight and blood pressure management in addition to glycemic control, and have drawn attention as a treatment option for high-risk patients as benefits have been reported in those with significant cardiac and renal risk. GLP-1 receptor agonists are therapies that lower blood glucose by enhancing the action of hormones that promote postprandial insulin secretion. Professor Jae-Hyun Bae of Seoul National University College of Medicine, who delivered the first lecture on Day 1, explained, “Metformin still remains an important drug in diabetes treatment, but the new guidelines have shifted away from a blood glucose–centric approach toward prioritizing drugs such as SGLT-2 inhibitors that can reduce the risks of cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and kidney disease in high-risk groups.”
Professor Jong-Han Choi of Konkuk University School of Medicine stated, “The fundamental framework of modern diabetes care is moving away from a traditional approach that looked only at blood glucose levels, toward one that incorporates patient characteristics such as comorbidities, body habitus, and lifestyle,” adding, “The trend of prioritizing SGLT-2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists when comorbidities are present has become more evident.”
Professor Young-Min Cho of Seoul National University College of Medicine presented the latest research trends regarding SGLT-2 inhibitors. He noted, “Aging is a major factor that reduces the body’s responsiveness to insulin, and it is intriguing that preclinical study results suggest SGLT-2 inhibitors may influence aging-related changes independently of their blood glucose–lowering effects.”
Professor Yeo-Ri Yang of The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine speaks at Daewoong Pharmaceutical’s 4D Symposium.
Latest blood glucose management strategy “Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)” presented… more precise care
On the second day, the latest blood glucose management strategies using Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) were introduced. In general, average indicators such as glycated hemoglobin (A1c, HbA1c) are used to assess glycemic control, but average values alone have limitations in fully capturing the fluctuations and patterns of blood glucose throughout the day. CGM is a technology that continuously tracks changes in blood glucose through a sensor. It is characterized by enabling more precise identification of glycemic variability and hypoglycemia risk and by its utility in management. In addition, there were forecasts that it will evolve into digital, integrated management, such as linkage with automated insulin delivery systems in the future.Professor Sang-Soo Kim of Pusan National University School of Medicine said, “Glycated hemoglobin reflects only average blood glucose and is not sufficient to capture glycemic variability or hypoglycemia risk,” and added, “CGM allows continuous monitoring of blood glucose trends and can help provide more multidimensional management.” Professor Yeo-Ri Yang of The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine emphasized that CGM is a tool that complements the limitations of conventional blood glucose measurements and projected that its scope of use will expand as technology advances.
Park Hyeong-Cheol, Head of ETC Marketing at Daewoong Pharmaceutical, stated, “The 4D Symposium is an academic, discussion-based platform designed to enable medical professionals to jointly interpret and discuss key issues in clinical practice, such as changes in treatment guidelines,” adding, “In this symposium, we reviewed drug selection criteria based on patient status and comorbidities following the guideline revisions and discussed a variety of initial treatment strategies tailored to patient characteristics.” He continued, “Going forward, Daewoong Pharmaceutical will continue to expand the sharing of the latest insights and will provide ongoing academic support and information sharing so that the evolving treatment environment can be reflected in actual clinical practice.”
Kim Min-beom
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News