Medical / Medical Device
Precision, Speed: Robotic Surgery Tailored for Patients
Dong-A Ilbo |
Updated 2025.11.26
As precision medicine advances, robotic surgery transforms joint treatment
〈1〉 Total knee arthroplasty
Increasing number of sports enthusiasts like hikers, runners, and golfers leads to a rise in middle-aged knee pain patients
Stage 4 deformity requires artificial replacement
Robotic surgery minimizes bone cutting and tissue damage, offering high accuracy and fast recovery as advantages
〈1〉 Total knee arthroplasty
Increasing number of sports enthusiasts like hikers, runners, and golfers leads to a rise in middle-aged knee pain patients
Stage 4 deformity requires artificial replacement
Robotic surgery minimizes bone cutting and tissue damage, offering high accuracy and fast recovery as advantages
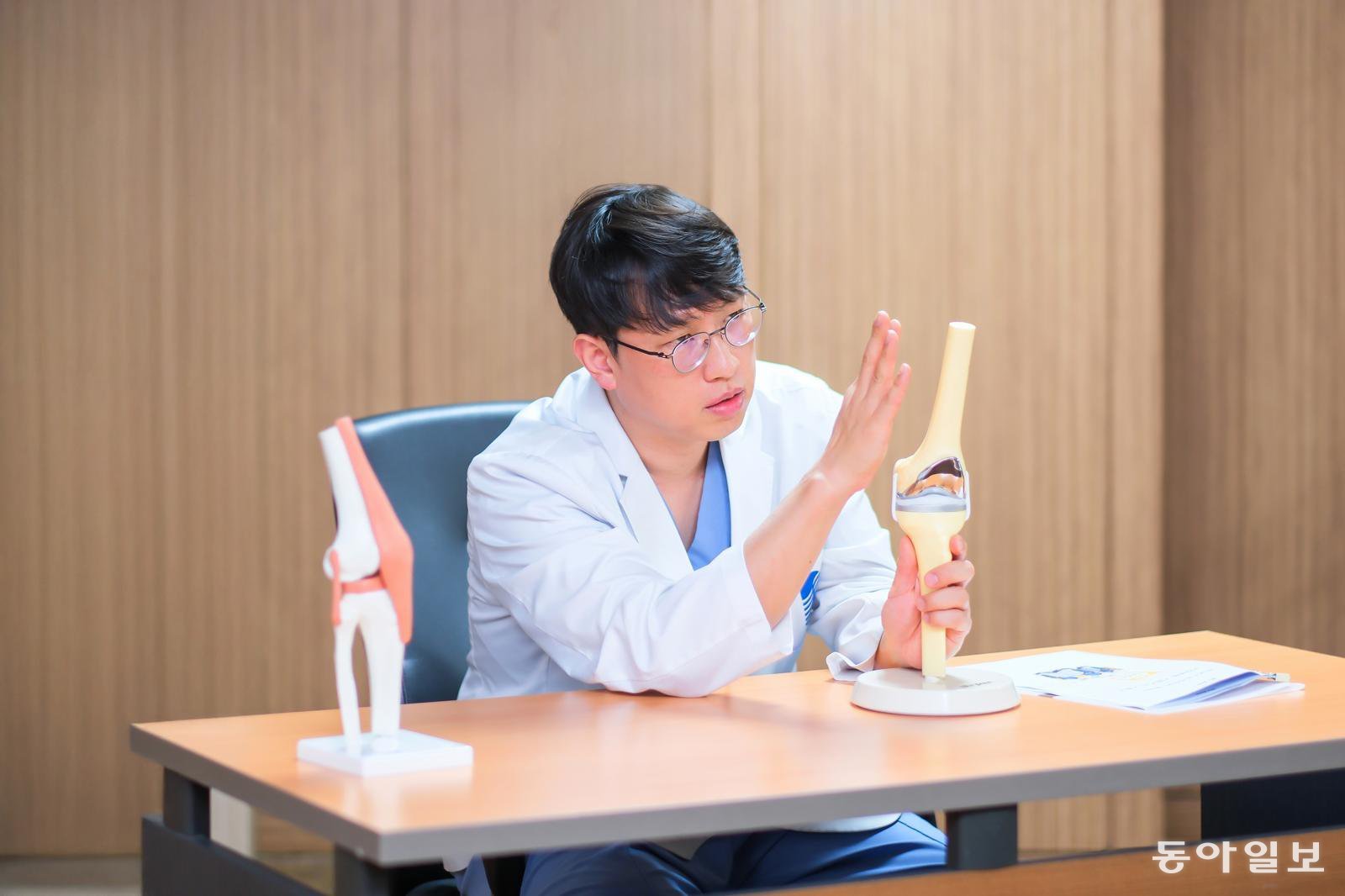
Director Lim Young-jae of Bogang Hospital explains robotic knee joint replacement surgery. Reporter Lee Doo-yong music@murepa.com
《As the number of patients with joint diseases rapidly increases due to aging and increased physical activity, the standards for treatment are also changing quickly. In particular, in the field of joint replacement surgery, the full-scale introduction of robotic technology is elevating the precision, safety, and recovery speed of surgeries to a new level. This publication conducts an in-depth analysis over three articles on how robotic surgery is transforming knee and hip treatments. The first article focuses on the changes brought about by robotic surgery in total knee replacement.》The number of patients with degenerative arthritis is steadily increasing due to aging. Additionally, activities that heavily use the knees, such as hiking and golf, have become commonplace, leading to a noticeable rise in cases of knee pain among the middle-aged group in their 50s and 60s. Artificial joint replacement surgery has become a representative treatment method for restoring damaged joint function. Recently, 'precision joint surgery' utilizing robotic systems is rapidly spreading and emerging as a new standard. Director Lim Young-jae of Bogang Hospital emphasized the importance of personalized treatment, stating, “Robotic surgery enhances the consistency and accuracy of results, thereby increasing patient satisfaction.”
―What are the reasons for the increase in patients with degenerative arthritis?
“Degenerative arthritis is a representative geriatric disease, but recently the age group of patients is becoming younger. In the past, most patients were in their 70s or older, but nowadays, the proportion of patients in their 50s and 60s, who engage in high-activity sports like hiking, golf, and jogging, is rapidly increasing. Repeated impacts, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles accumulate micro-damage to the joints, resulting in more patients experiencing knee pain at a relatively early age.”
―What is degenerative arthritis, and when is surgery necessary?
“It is a chronic disease where the cartilage wears out and the joint surface deforms, causing pain, swelling, and movement restrictions. In the early stages, symptoms can be controlled with non-surgical treatments such as medication, injections, and physical therapy. However, in the fourth stage, where the damage is severe, the joint space is nearly gone, or leg deformity progresses, joint replacement surgery is necessary. Early diagnosis is crucial. It is essential not to dismiss pain as mere aging but to establish an optimal treatment strategy through accurate diagnosis to preserve joint function.”
―What is the principle behind joint replacement surgery?
“The principle involves cutting away the damaged joint surface and inserting an artificial joint made of special metal material at an accurate angle to restore the alignment of the joint. When the imbalance of the joint is corrected, the friction between bones is reduced, alleviating pain and increasing stability by reducing wobbling during walking. The purpose of the surgery is not merely to eliminate pain but to restore the ‘function’ of the joint.”
―Why is robotic joint surgery gaining attention recently?
“Traditional surgery heavily relied on the surgeon’s experience and intuition. In contrast, robotic surgery can implement a 3D knee structure based on the patient’s computed tomography (CT) and pre-plan the cutting range and implant position. During surgery, haptic control ensures that the robotic arm only cuts within the planned range, minimizing unnecessary bone cutting or soft tissue damage. This results in higher accuracy and faster recovery.”
―Has the role of medical staff changed with the introduction of robots?
“In the past, the doctor’s experience and tactile sense were central, but now the role of ‘designer’ who sets precise plans and compares them with real-time data to perform optimal cutting is expanding. The most significant change is that standardization of surgery has become possible thanks to robots. The variance due to differences in proficiency has decreased, and reproducibility has greatly improved. Consequently, a more reliable environment has been created for patients.”
―What does ‘patient-customized surgery,’ the core of robotic surgery, mean?
“Each patient has different bone shapes, degrees of deformation, and ligament tension. Robotic surgery can precisely analyze these anatomical differences through CT-based 3D modeling and finely adjust the cutting depth and implant angle. As a result, postoperative movements are natural, and joint stability is enhanced. This is why patients express that ‘the knee fits my body perfectly.’”
―Which patients are particularly effective candidates for robotic surgery?
“Not all patients require surgery. Early-stage degenerative arthritis can be sufficiently managed with non-surgical treatments. However, robotic surgery is highly beneficial for patients in the fourth stage with persistent pain and nearly absent joint space, patients with misaligned legs, and those with severe deformities. Additionally, patients who need sequential surgery on both knees or those whose anatomical structure has changed due to past surgeries can benefit from the precise planning of robots.”
―Has there been a change in prognosis or patient satisfaction since the introduction of the robotic system?
“The most noticeable aspect is the consistency of results. When using robots, the cutting range and alignment are executed precisely as planned, reducing postoperative pain and swelling and accelerating recovery. Elderly patients are more engaged in rehabilitation and often respond positively, saying ‘recovery is faster than expected.’ For patients, it is perceived as a more comfortable and less daunting surgery, and for medical staff, it provides predictable and stable results, which is the most significant change.”
Hong Eun-sim
AI-translated with ChatGPT. Provided as is; original Korean text prevails.
ⓒ dongA.com. All rights reserved. Reproduction, redistribution, or use for AI training prohibited.
Popular News